207
2467S–AVR–07/09
ATmega128
• Bit 4 – TWSTO: TWI STOP Condition Bit
Writing the TWSTO bit to one in Master mode will generate a STOP condition on the Two-wire
Serial Bus. When the STOP condition is executed on the bus, the TWSTO bit is cleared auto-
matically. In slave mode, setting the TWSTO bit can be used to recover from an error condition.
This will not generate a STOP condition, but the TWI returns to a well-defined unaddressed
Slave mode and releases the SCL and SDA lines to a high impedance state.
• Bit 3 – TWWC: TWI Write Collision Flag
The TWWC bit is set when attempting to write to the TWI Data Register – TWDR when TWINT is
low. This flag is cleared by writing the TWDR Register when TWINT is high.
• Bit 2 – TWEN: TWI Enable Bit
The TWEN bit enables TWI operation and activates the TWI interface. When TWEN is written to
one, the TWI takes control over the I/O pins connected to the SCL and SDA pins, enabling the
slew-rate limiters and spike filters. If this bit is written to zero, the TWI is switched off and all TWI
transmissions are terminated, regardless of any ongoing operation.
• Bit 1 – Res: Reserved Bit
This bit is a reserved bit and will always read as zero.
• Bit 0 – TWIE: TWI Interrupt Enable
When this bit is written to one, and the I-bit in SREG is set, the TWI interrupt request will be acti-
vated for as long as the TWINT flag is high.
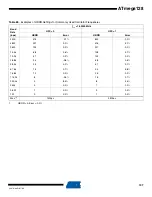
TWI Status Register –
TWSR
• Bits 7..3 – TWS: TWI Status
These 5 bits reflect the status of the TWI logic and the Two-wire Serial Bus. The different status
codes are described later in this section. Note that the value read from TWSR contains both the
5-bit status value and the 2-bit prescaler value. The application designer should mask the pres-
caler bits to zero when checking the Status bits. This makes status checking independent of
prescaler setting. This approach is used in this datasheet, unless otherwise noted.
• Bit 2 – Res: Reserved Bit
This bit is reserved and will always read as zero.
• Bits 1..0 – TWPS: TWI Prescaler Bits
These bits can be read and written, and control the bit rate prescaler.
To calculate bit rates, see
“Bit Rate Generator Unit” on page 204
. The value of TWPS1..0 is
used in the equation.
Bit
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
TWS7
TWS6
TWS5
TWS4
TWS3
–
TWPS1
TWPS0
TWSR
Read/Write
R
R
R
R
R
R
R/W
R/W
Initial Value
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
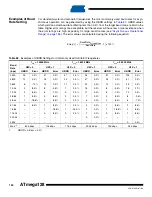
Table 87.
TWI Bit Rate Prescaler
TWPS1
TWPS0
Prescaler Value
0
0
1
0
1
4
1
0
16
1
1
64