122
2467S–AVR–07/09
ATmega128
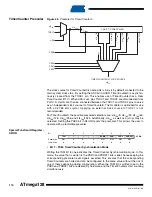
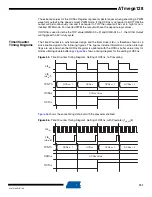
The OCRnx Register access may seem complex, but this is not case. When the double buffering
is enabled, the CPU has access to the OCRnx buffer register, and if double buffering is disabled
the CPU will access the OCRnx directly. The content of the OCR1x (buffer or compare) register
is only changed by a write operation (the Timer/Counter does not update this register automati-
cally as the TCNTn- and ICRn Register). Therefore OCRnx is not read via the high byte
Temporary Register (TEMP). However, it is a good practice to read the low byte first as when
accessing other 16-bit registers. Writing the OCRnx registers must be done via the TEMP Regis-
ter since the compare of all 16 bits is done continuously. The high byte (OCRnxH) has to be
written first. When the high byte I/O location is written by the CPU, the TEMP Register will be
updated by the value written. Then when the low byte (OCRnxL) is written to the lower 8 bits, the
high byte will be copied into the upper 8 bits of either the OCRnx buffer or OCRnx Compare
Register in the same system clock cycle.
For more information of how to access the 16-bit registers refer to
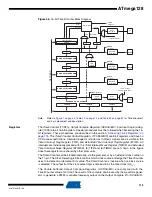
Force Output
Compare
In non-PWM Waveform Generation modes, the match output of the comparator can be forced by
writing a one to the
Force Output Compare
(FOCnx) bit. Forcing compare match will not set the
OCFnx flag or reload/clear the timer, but the OCnx pin will be updated as if a real compare
match had occurred (the COMnx1:0 bits settings define whether the OCnx pin is set, cleared or
toggled).
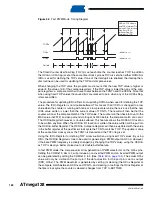
Compare Match
Blocking by TCNTn
Write
All CPU writes to the TCNTn Register will block any compare match that occurs in the next timer
clock cycle, even when the timer is stopped. This feature allows OCRnx to be initialized to the
same value as TCNTn without triggering an interrupt when the Timer/Counter clock is enabled.
Using the Output
Compare Unit
Since writing TCNTn in any mode of operation will block all compare matches for one timer clock
cycle, there are risks involved when changing TCNTn when using any of the output compare
channels, independent of whether the Timer/Counter is running or not. If the value written to
TCNTn equals the OCRnx value, the compare match will be missed, resulting in incorrect wave-
form generation. Do not write the TCNTn equal to TOP in PWM modes with variable TOP
values. The compare match for the TOP will be ignored and the counter will continue to 0xFFFF.
Similarly, do not write the TCNTn value equal to BOTTOM when the counter is downcounting.
The setup of the OCnx should be performed before setting the Data Direction Register for the
port pin to output. The easiest way of setting the OCnx value is to use the force output compare
(FOCnx) strobe bits in normal mode. The OCnx Register keeps its value even when changing
between waveform generation modes.
Be aware that the COMnx1:0 bits are not double buffered together with the compare value.
Changing the COMnx1:0 bits will take effect immediately.