184
2467S–AVR–07/09
ATmega128
Parity Checker
The parity checker is active when the high USART Parity mode (UPM1) bit is set. Type of parity
check to be performed (odd or even) is selected by the UPM0 bit. When enabled, the parity
checker calculates the parity of the data bits in incoming frames and compares the result with
the parity bit from the serial frame. The result of the check is stored in the receive buffer together
with the received data and stop bits. The Parity Error (UPE) flag can then be read by software to
check if the frame had a Parity Error.
The UPE bit is set if the next character that can be read from the receive buffer had a parIty
Error when received and the parity checking was enabled at that point (UPM1 = 1). This bit is
valid until the Receive buffer (UDR) is read.
Disabling the Receiver
In contrast to the Transmitter, disabling of the Receiver will be immediate. Data from ongoing
receptions will therefore be lost. When disabled (i.e., the RXEN is set to zero) the receiver will no
longer override the normal function of the RxD port pin. The receiver buffer FIFO will be flushed
when the receiver is disabled. Remaining data in the buffer will be lost
Flushing the Receive
Buffer
The receiver buffer FIFO will be flushed when the receiver is disabled, i.e. the buffer will be emp-
tied of its contents. Unread data will be lost. If the buffer has to be flushed during normal
operation, due to for instance an error condition, read the UDR I/O location until the RXC flag is
cleared. The following code example shows how to flush the receive buffer.
Note:
1. See “About Code Examples” on page 9..
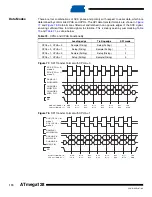
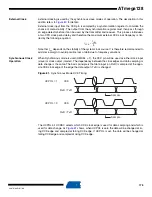
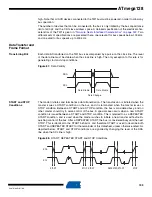
The USART includes a clock recovery and a data recovery unit for handling asynchronous
data reception. The clock recovery logic is used for synchronizing the internally generated
baud rate clock to the incoming asynchronous serial frames at the RxD pin. The data recovery
logic samples and low pass filters each incoming bit, thereby improving the noise immunity of
the receiver. The asynchronous reception operational range depends on the accuracy of the
internal baud rate clock, the rate of the incoming frames, and the frame size in number of bits.
Assembly Code Example
USART_Flush:
sbis
UCSRA, RXC
ret
in
r16, UDR
rjmp
USART_Flush
C Code Example
void
USART_Flush(
void
)
{
unsigned char
dummy;
while
( UCSRA & (1<<RXC) ) dummy = UDR;
}