119
2467S–AVR–07/09
ATmega128
are generated on the output compare outputs OCnx. For more details about advanced counting
sequences and waveform generation, see
“Modes of Operation” on page 124
.
The
Timer/Counter Overflow
(TOVn) flag is set according to the mode of operation selected by
the WGMn3:0 bits. TOVn can be used for generating a CPU interrupt.
Input Capture Unit
The Timer/Counter incorporates an Input Capture unit that can capture external events and give
them a time-stamp indicating time of occurrence. The external signal indicating an event, or mul-
tiple events, can be applied via the ICPn pin or alternatively, for the Timer/Counter1 only, via the
Analog Comparator unit. The time-stamps can then be used to calculate frequency, duty-cycle,
and other features of the signal applied. Alternatively the time-stamps can be used for creating a
log of the events.
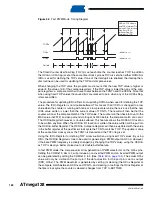
The Input Capture unit is illustrated by the block diagram shown in
. The elements of
the block diagram that are not directly a part of the Input Capture unit are gray shaded. The
small “n” in register and bit names indicates the Timer/Counter number.
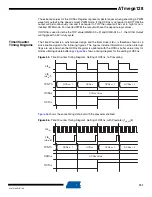
Figure 48.
Input Capture Unit Block Diagram
Note:
The Analog Comparator Output (ACO) can only trigger the Timer/Counter1 ICP – not
Timer/Counter3.
When a change of the logic level (an event) occurs on the
Input Capture Pin
(ICPn), alternatively
on the
analog Comparator output
(ACO), and this change confirms to the setting of the edge
detector, a capture will be triggered. When a capture is triggered, the 16-bit value of the counter
(TCNTn) is written to the
Input Capture Register
(ICRn). The
Input Capture Flag
(ICFn) is set at
the same system clock as the TCNTn value is copied into ICRn Register. If enabled (TICIEn =
1), the Input Capture flag generates an Input Capture interrupt. The ICFn flag is automatically
cleared when the interrupt is executed. Alternatively the ICFn flag can be cleared by software by
writing a logical one to its I/O bit location.
Reading the 16-bit value in the
Input Capture Register
(ICRn) is done by first reading the low
byte (ICRnL) and then the high byte (ICRnH). When the low byte is read the high byte is copied
ICFn
(Int.Req.)
Analog
Comparator
WRITE
ICRn
(16-bit Register)
ICRnH
(8-bit)
Noise
Canceler
ICPn
Edge
Detector
TEMP
(8-bit)
DATA BUS
(8-bit)
ICRnL
(8-bit)
TCNTn
(16-bit Counter)
TCNTnH
(8-bit)
TCNTnL
(8-bit)
ACIC*
ICNC
ICES
ACO*