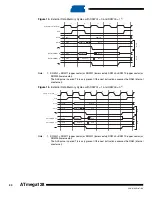
43
2467S–AVR–07/09
ATmega128
to the register gives the highest available frequency. The calibrated Oscillator is used to time
EEPROM and Flash access. If EEPROM or Flash is written, do not calibrate to more than 10%
above the nominal frequency. Otherwise, the EEPROM or Flash write may fail. Note that the
Oscillator is intended for calibration to 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, or 8.0 MHz. Tuning to other values is not
guaranteed, as indicated in
.
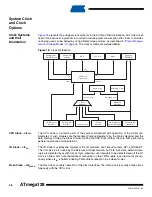
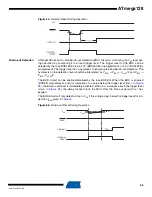
External Clock
To drive the device from an external clock source, XTAL1 should be driven as shown in
. To run the device on an external clock, the CKSEL fuses must be programmed to “0000”. By
programming the CKOPT fuse, the user can enable an internal 36 pF capacitor between XTAL1
and GND.
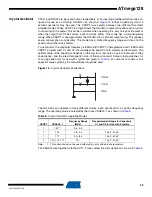
Figure 21.
External Clock Drive Configuration
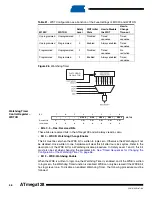
When this clock source is selected, start-up times are determined by the SUT fuses as shown in
When applying an external clock, it is required to avoid sudden changes in the applied clock fre-
quency to ensure stable operation of the MCU. A variation in frequency of more than 2% from
one clock cycle to the next can lead to unpredictable behavior. It is required to ensure that the
MCU is kept in Reset during such changes in the clock frequency.
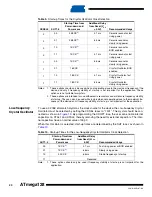
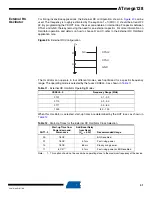
Table 15.
Internal RC Oscillator Frequency Range.
OSCCAL Value
Min Frequency in Percentage of
Nominal Frequency (%)
Max Frequency in Percentage of
Nominal Frequency (%)
$00
50
100
$7F
75
150
$FF
100
200
Table 16.
Start-up Times for the External Clock Selection
SUT1..0
Start-up Time from Power-
down and Power-save
Additional Delay from
Reset (V
CC
= 5.0V)
Recommended Usage
00
6 CK
–
BOD enabled
01
6 CK
4.1 ms
Fast rising power
10
6 CK
65 ms
Slowly rising power
11
Reserved
EXTERNAL
CLOCK
SIGNAL