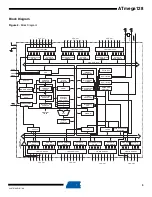
5
2467S–AVR–07/09
ATmega128
ATmega103
Compatibility Mode
By programming the M103C fuse, the ATmega128 will be compatible with the ATmega103
regards to RAM, I/O pins and interrupt vectors as described above. However, some new fea-
tures in ATmega128 are not available in this compatibility mode, these features are listed below:
•
One USART instead of two, Asynchronous mode only. Only the eight least significant bits of
the Baud Rate Register is available.
•
One 16 bits Timer/Counter with two compare registers instead of two 16-bit Timer/Counters
with three compare registers.
•
Two-wire serial interface is not supported.
•
Port C is output only.
•
Port G serves alternate functions only (not a general I/O port).
•
Port F serves as digital input only in addition to analog input to the ADC.
•
Boot Loader capabilities is not supported.
•
It is not possible to adjust the frequency of the internal calibrated RC Oscillator.
•
The External Memory Interface can not release any Address pins for general I/O, neither
configure different wait-states to different External Memory Address sections.
In addition, there are some other minor differences to make it more compatible to ATmega103:
•
Only EXTRF and PORF exists in MCUCSR.
•
Timed sequence not required for Watchdog Time-out change.
•
External Interrupt pins 3 - 0 serve as level interrupt only.
•
USART has no FIFO buffer, so data overrun comes earlier.
Unused I/O bits in ATmega103 should be written to 0 to ensure same operation in ATmega128.
Pin Descriptions
VCC
Digital supply voltage.
GND
Ground.
Port A (PA7..PA0)
Port A is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port A output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port A pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port A pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port A also serves the functions of various special features of the ATmega128 as listed on
.
Port B (PB7..PB0)
Port B is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port B output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port B pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port B pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port B also serves the functions of various special features of the ATmega128 as listed on
.
Port C (PC7..PC0)
Port C is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port C output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port C pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up