NBC™ Flat Belt - IOM
P/N: 1118140
Rev: 07/29/2020
Page
93
of
129
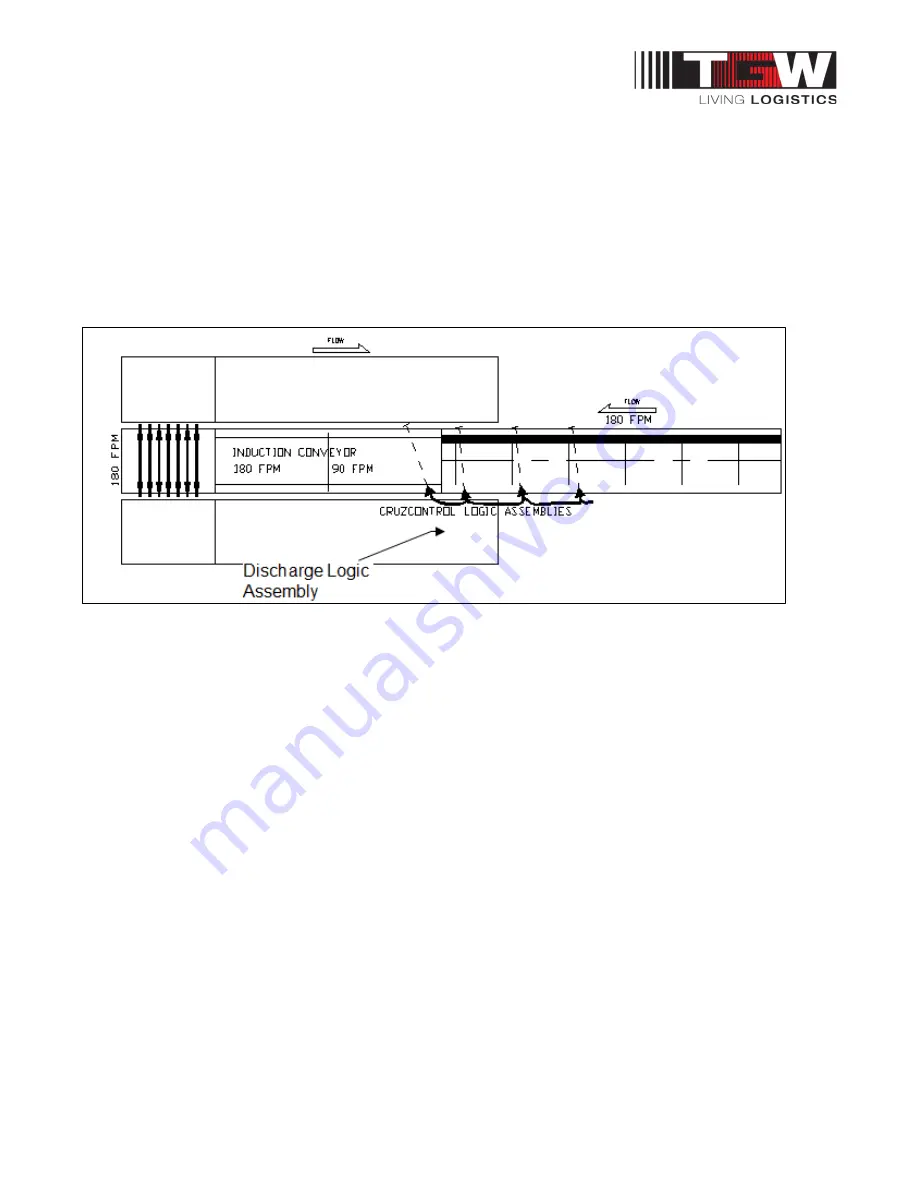
Example
The NBC is running at 180 FPM, feeding the induction conveyor section prior to a pick zone module
diverter. Without proper control of the discharge from the NBC, cartons released to the induction
conveyor could possibly overdrive it and push past the 90 FPM section onto the 180 FPM section, not
permitting product gapping to occur as required for the diverter to function properly.
The mounting location of the Discharge Logic Assembly photoelectric sensor and the reflector will
determine release performance. A good starting point would be to locate the photoelectric sensor 12"
downstream from the charge end of the induction conveyor, and the reflector 18" downstream from
the charge end. The final locations should be determined based on system performance.
Example 4: Product Gapping
The following describes a technique, using CRUZcontrol, which creates a gap in a train of moving
product. In the situation described, the gap is used to allow for the raising of a product stop. This
would apply primarily to the progressive mode of accumulation control, which accumulates and
discharges from accumulation with only minimal gaps between products.
The following illustrates an NBC accumulation lane used to release product to a merge conveyor. A
Product Stop is located at the end of the accumulation lane, controlled by the solenoid valve as
shown. The last two accumulation zones are also provided with brakes, as shown. These brakes are
controlled by the CRUZcontrol Logic Assemblies that also control the zone drive. Also shown just prior
to the Product Stop is a Product Present Photosensor.






























