www.ti.com
9.3.3
TCI6482 PCI vs TCI100 PCI
9.4
Multichannel Buffered Section Port (McBSP)
9.4.1
Configuration of McBSP
9.4.2
System Implementation of McBSP
Peripheral Section
Operating PCI at 66MHz has tight timing requirements and should only be implemented for point-to-point
implementations.
The PCI specification gives sufficient guidelines that if followed, simulations are unnecessary. But if the
PCI specification guidelines are not followed or there is something unique in the implementation, IBIS
models are provided so simulations can be run.
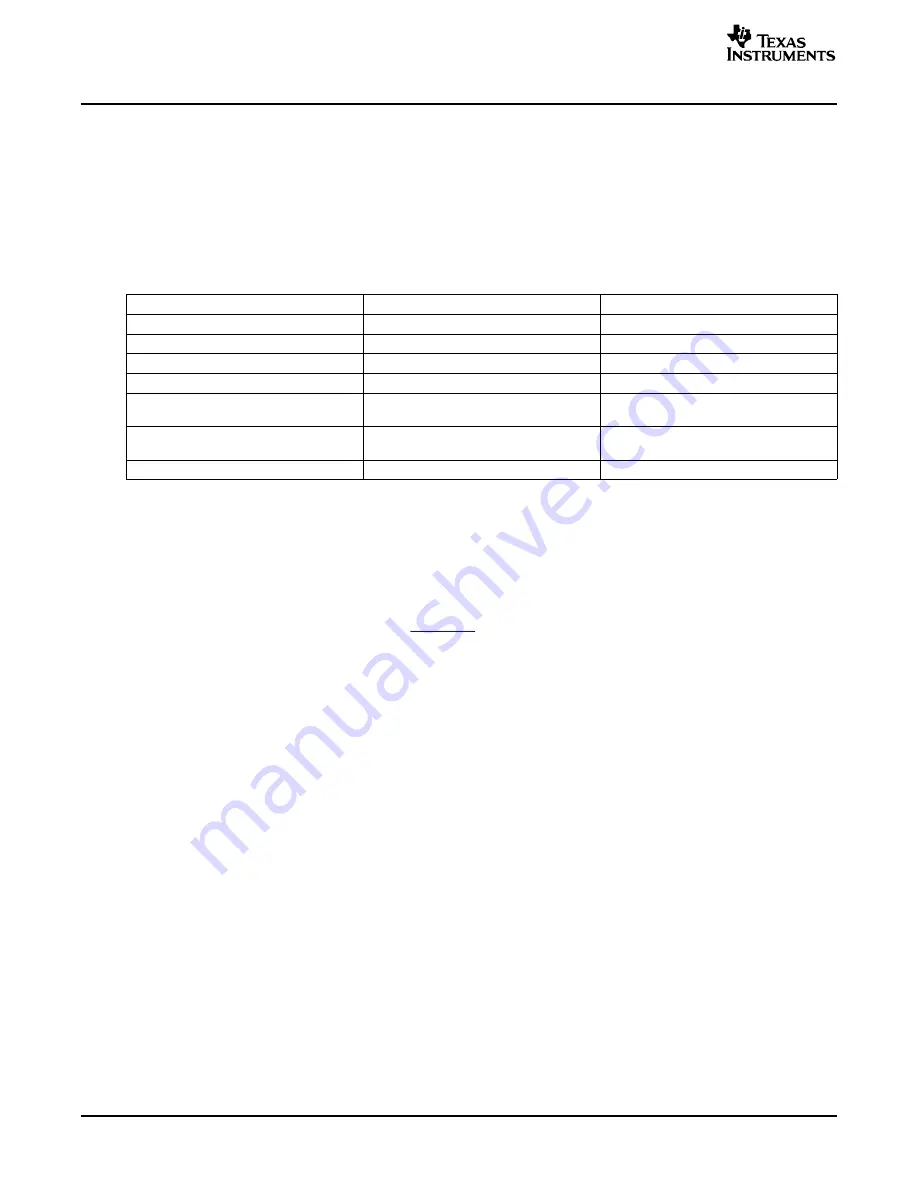
Table 13. PCI Comparison: TCI6482 vs TCI100
TCI6482
TCI100
Default condition (if selected)
Disabled
Enabled
PCI Conformance
PCI Specification Revision 2.3
PCI Specification Revision 2.2
Operating Frequency
33MHz or 66MHz
33MHz
PCI Auto-Initialization Interface
I2C ROM
McBSP to SPI ROM
Target Window (outbound transfers)
32 8MB programmable target windows
1 fixed target window. Maximum of single
mapped to DSP memory space.
64MB transfer.
Target Window (inbound transfers)
6 base programmable windows unlimited
3 fixed base addresses
access range.
Supports Boot over PCI
ü
ü
Documentation for McBSP:
•
TMS320TCI648x DSP Multichannel Buffered Serial Port ( McBSP) Reference Guide (SPRU803)
•
TCI6482 IBIS Model File
•
Using IBIS Modes for Timing Analysis (
SPRA839
)
McBSP0 and McBSP1 are multiplexed with the VLYNQ peripheral and a boot strapping option is used to
select between them. Another strapping option selects between McBSP1 and GPIO pins. After a reset,
software must enable the McBSP interface(s).
The McBSP module receives SYSCLK3 as its input clock, which runs at the CPU core clock / 6. The
McBSP port clocks can either be driven by an external clock (CLKS) or by an internal clock which is
derived from SYSCLK3. There is only one CLKS input which supplies both McBSP ports, but both ports
can individually be programmed to use internal or external (CLKS) clocks.
If the internal clock is selected, the minimum divisor is /2. For example, if the core clock is 1GHz then
SYSCLK3 is 166MHz and the maximum McBSP clock is 83MHz.
If a McBSP port is not used or some of the signals are not used, the pins can be left unconnected since
internal pull-ups/downs are included. The CLKS also has an internal pull-down so that it may be left
unconnected if not used.
The maximum McBSP performance is achievable only when using source synchronous modes and
point-to-point connections. In this case, series resistance should be used to reduce over/under-shoot.
Generally acceptable values are 10, 22 or 33 ohms. To determine the optimum value simulations using
the IBIS models should be performed to check signal integrity and AC timings.
Multiple DSPs can be connected to a common McBSP bus using TDM mode. The additional loads will
require a reduction in the operating frequency. Also, the specific routing topology becomes much more
significant as additional DSPs are included. The way to determine the best topology and maximum
operating frequency are by performing IBIS simulations.
26
TMS320TCI6482 Design Guide and Migration from TMS320TCI100
SPRAAC7B – April 2006
Submit Documentation Feedback






























