Chapter 15. The PID functions
15-2
15.2 PID control
15.2.1
Control actions
15.2.1.1
Proportional operation (P operation)
1) P action means a control action that obtain a manipulate value which is proportional
to the deviation (E : the difference between SV and PV)
2) The deviation (E) is obtained by multiplying a reference value to the actual
difference between SV and PV. It prevents the deviation from a sudden change or
alteration caused by external disturbance. The formula of deviation is as following;
[
]
PV
SV
b
Kp
MV
−
×
×
=
Kp
: the proportional constant (gain)
b
: reference value
SV
: set value
PV
: present value
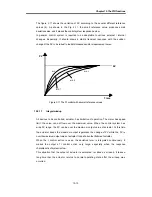
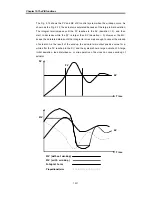
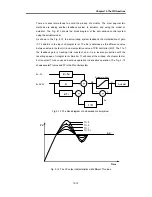
3) If the Kp is too large, the PV reaches to the SV swiftly, but it may causes a bad
effect like oscillations shown in the Fig. 2.1.
4) If the Kp is too small, oscillation will not occur. However, the PV reaches to the SV
slowly and an offset may appear between PV and SV shown in the Fig. 2.2.
5) The manipulation value (MV) varies from 0 to 4,000. User can define the maximum
value of MV (MV_MAX) and minimum value (MV_MIN) within the range 0 ~ 4,000.
6) When an offset remains after the system is stabilized, the PV can be reached to the
SV by adding a certain value. This value is called as bias value, and user can
define the bias value with GM-WIN software.
Содержание GLOFA GM6 Series
Страница 1: ...U s e r s M a n u a l LG Programmable Logic Controller GLOFA GM6 Series L G Industrial Systems ...
Страница 2: ... CONTENTS ...
Страница 178: ...Chapter 15 The PID functions 15 24 Example program of 15 4 3 1 ...
Страница 179: ...Chapter 15 The PID functions 15 25 Example program of 15 4 3 2 continue to next page ...
Страница 180: ...Chapter 15 The PID functions 15 26 Example program of 15 4 3 2 continued ...
Страница 209: ...Appendix 4 Outer Dimensions APP4 3 ...