E
S.E.C. CARTRIDGE MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS
11-11
8/29/97 11:15 AM CH11.DOC
INTEL CONFIDENTIAL
(until publication date)
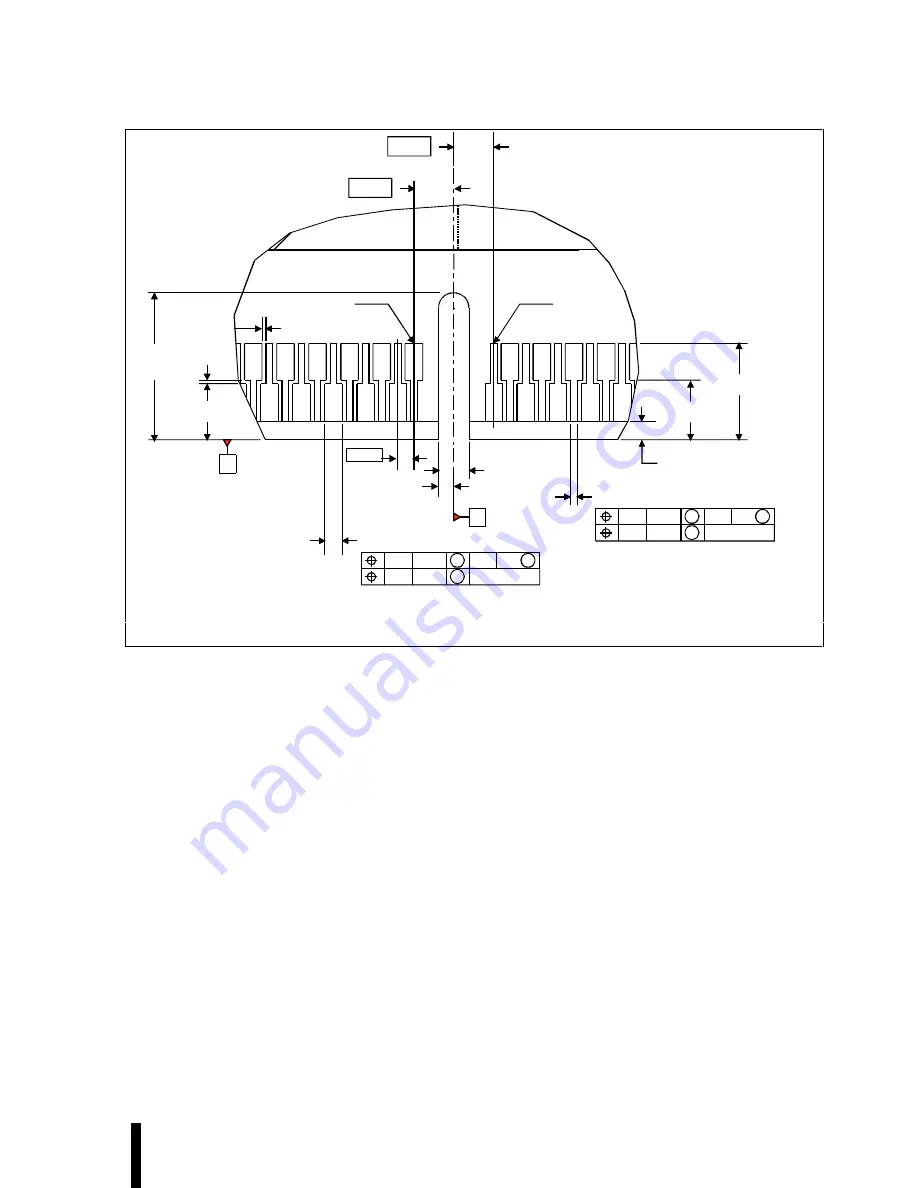
0.146 Max.
0.098
Y
Pin A74
Pin A73
0.098
W
0.039
0.037
121 X 0.016 ±0.002
0.045
0.236
0.074 ±0.002
.20 .008
L
Z
W M
.05 .002
Pad to Pad
121 X 0.043 ±0.002
.20 .008
L
Z
W M
.05 .002
Pad to Pad
L
L
0.356
Min.
0.138 Min.
0.008
(0.010)
001060b
NOTE:
All dimensions without tolerance information are considered reference dimensions only.
Figure 11-11. S.E.C. Cartridge Substrate—Detail A
Содержание Pentium II
Страница 1: ...D Pentium II Processor Developer s Manual 243502 001 October 1997 1997...
Страница 11: ...E 1 Component Introduction...
Страница 12: ......
Страница 17: ...E 2 Micro Architecture Overview...
Страница 18: ......
Страница 33: ...E 3 System Bus Overview...
Страница 34: ......
Страница 45: ...E 4 Data Integrity...
Страница 46: ......
Страница 51: ...E 5 Configuration...
Страница 52: ......
Страница 62: ......
Страница 63: ...E 6 Test Access Port TAP...
Страница 64: ......
Страница 75: ...E 7 Electrical Specifications...
Страница 76: ......
Страница 106: ......
Страница 107: ...E 8 GTL Interface Specifications...
Страница 108: ......
Страница 129: ...E 9 Signal Quality Specifications...
Страница 130: ......
Страница 136: ......
Страница 137: ...E 10 Thermal Specifications and Design Considerations...
Страница 138: ......
Страница 149: ...E 11 S E C Cartridge Mechanical Specifications...
Страница 150: ......
Страница 154: ...S E C CARTRIDGE MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS E 11 4 001055a Figure 11 2 S E C Cartridge Top and Side Views...
Страница 155: ...E S E C CARTRIDGE MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS 11 5 001054a Figure 11 3 S E C Cartridge Bottom Side View...
Страница 173: ...E 12 Boxed Processor Specifications...
Страница 174: ......
Страница 185: ...E 13 Integration Tools...
Страница 186: ......
Страница 202: ......
Страница 203: ...E 14 Advanced Features...
Страница 204: ......
Страница 206: ......
Страница 207: ...E A Signals Reference...
Страница 208: ......















































