Chapter 8 – Using the digital operator
8-5
Function Display
*
)
Function description / parameter setting range
Standard
setting
Analog set value adjustment
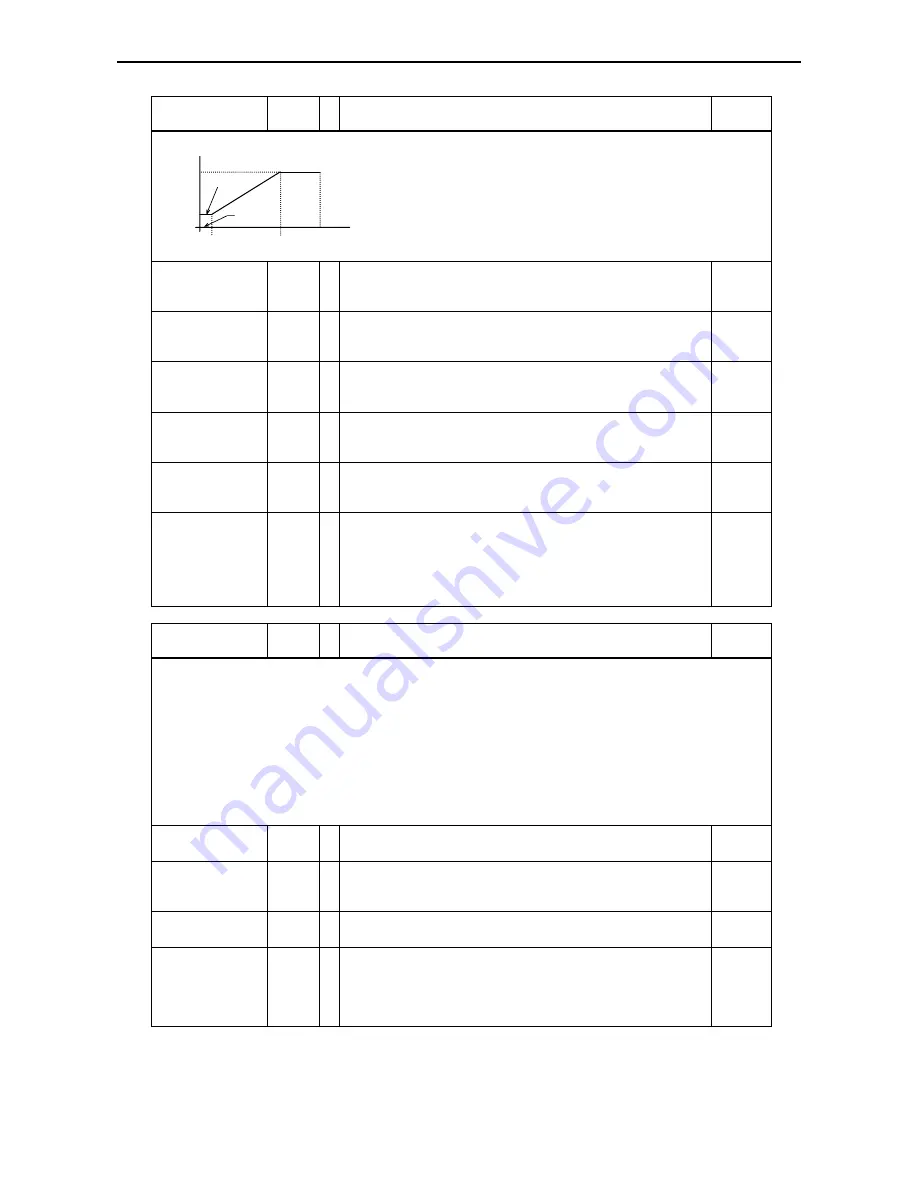
f
A 12
Analog input
voltage or
current set
value
A 11
20mA
A 14
A 13
0V
4mA
10V
A 15
= 01
A 15
= 00
External frequency
start point
A 11
N
Here the frequency is set that corresponds to the external frequency
start point bias set under
A 13
.
Setting range 0Hz–360Hz.
0.0
External frequency
end point
A 12
N
Here the frequency is set that corresponds to the external frequency
end point bias set under
A 13
.
Setting range 0Hz–360Hz.
0.0
External frequency
start point bias
A 13
N
The value entered here is based on the maximum voltage set value or
current set value of 10V or 20mA, respectively.
Setting range 0%–100%.
0
External frequency
end point bias
A 14
N
The value entered here is based on the maximum voltage set value or
current set value of 10V or 20mA, respectively.
Setting range 0%–100%.
100
External frequency
start pattern
A 15
N
Inverter behaviour for set values < external frequency start point:
00: The frequency configured under
A 11
is sent to the motor
01: A frequency of 0Hz is sent to the motor
01
Analog input filter
time constant
A 16
N
A value between 1 and 8 can be entered to configure the inverter’s
reaction speed to changes in analog set value at the O or OI terminal
and thus determine the amount of filtering for harmonics that may be
present with the analog signal:
1: Little filtering / fast reaction to changes in set value
8: Extensive filtering / slow reaction to changes in set value
8
Function Display
*
)
Function description / parameter setting range
Standard
setting
Multistage frequency settings and jogging mode
Up to 15 multistage frequency settings can be selected using the digital inputs configured as CF1 through CF4.
Alternatively to setting the multistage frequencies under functions
A 21
through
A 35
they can be set using function
F 01.
Jogging mode can be used to set up a machine manually and is activated using a digital input configured as JG.
Since the acceleration ramp is not active during jogging mode, there might be an overcurrent trip (especially when a
too high jogging frequency is chosen). Jogging mode can not be used when the jogging frequency is smaller than the
start frequency configured under
b 82
.
Multistage frequency settings have a higher priority than other frequency set values. Only the jogging frequency’s
priority is even higher.
Frequency
set value
A 20
Y
A frequency set value between 0.5Hz and 360Hz can be entered here (a
02 must have been configured under
A 01
beforehand).
0
Multistage frequency
settings
A 21
thru
A 35
Y
Any one of the 15 multistage frequency settings from
A 21
through
A 35
can be assigned a frequency in the range of 0.5Hz to 360Hz.
0
(any one)
Jogging frequency
A 38
Y
The frequency that is sent to the motor when jogging mode is activated
can be chosen from 0.5Hz to 9.99Hz.
1.0
Jogging stop mode
A 39
N
When a stop command is issued during activated jogging mode, the
motor stops by:
00: running free
01: decelerating using configured deceleration time
02: decelerating using DC brake
00
The external frequency set value can be individually adjusted
using functions
A 11
to
A 16
. A configurable voltage or
current set value range can be assigned to a configurable
frequency range.
Furthermore, the analog input signal filtering can be adjusted
using function
A 16
.
Содержание L100 IP Series
Страница 2: ......
Страница 14: ...Chapter 2 Inspection upon unpacking 2 2 ...
Страница 16: ...Chapter 3 Appearance and names of parts 3 2 ...
Страница 46: ...Chapter 7 Control circuit terminal functions 7 18 ...
Страница 74: ......
Страница 84: ......
















































