Chapter 21 Load Balancing
NWA-3160 Series User’s Guide
268
21.2.1 Disassociating and Delaying Connections
When your AP becomes overloaded, there are two basic responses it can take. The
first one is to “delay” a client connection. This means that the AP withholds the
connection until the data transfer throughput is lowered or the client connection is
picked up by another AP. If the client is picked up by another AP then the original
AP cannot resume the connection.
For example, here the AP has a balanced bandwidth allotment of 6 Mbps. If the
red laptop (
R
) attempts to connect and it could potentially push the AP over its
allotment, say to 7 Mbps, then the AP delays the red laptop’s connection until it
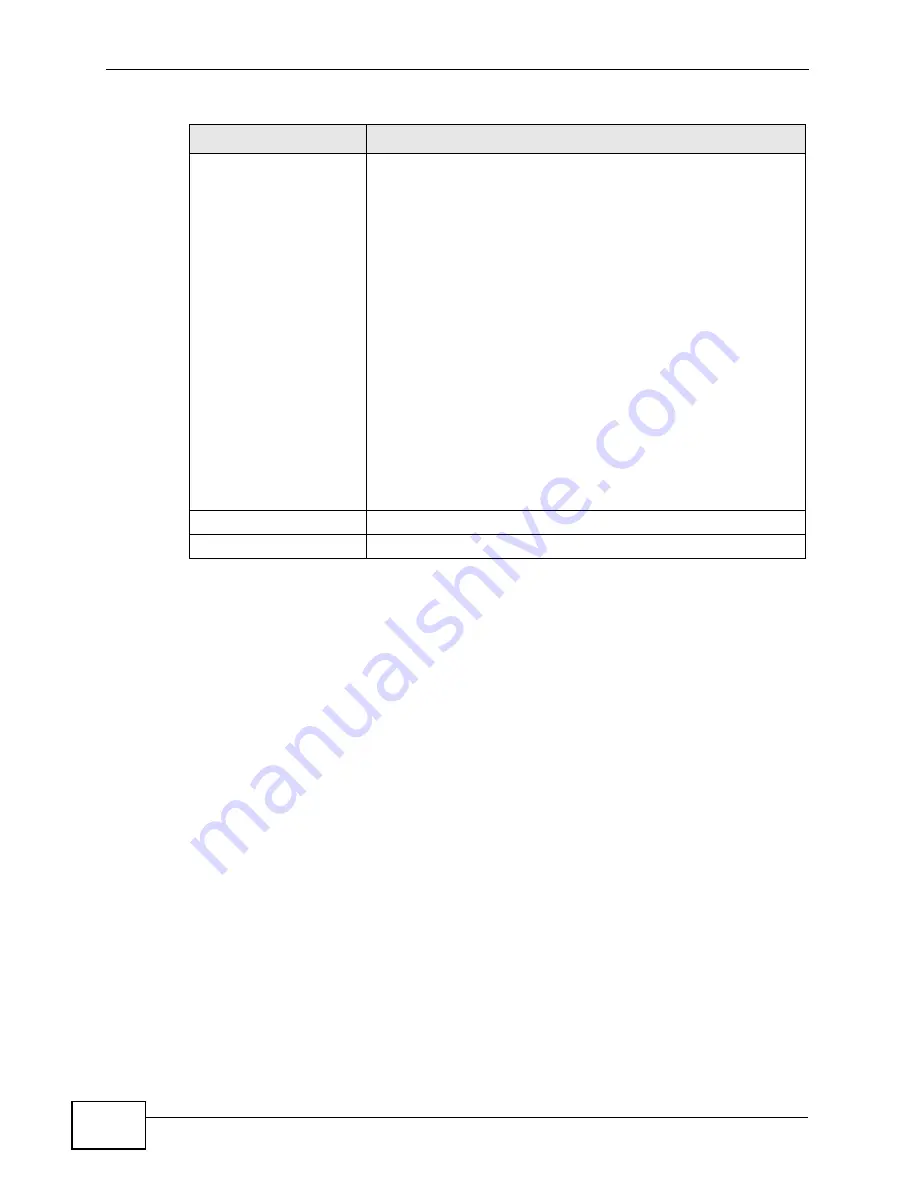
Dissociate station when
overloaded
Select
Enable
to “kick” connections to the AP when it becomes
overloaded. If you set this option to
Disable
, then the AP
simply delays the connection until it can afford the bandwidth
it requires, or it shunts the connection to another AP within its
broadcast radius.
The kick priority is determined automatically by the NWA and
is as follows:
•
Idle Timeout
- Devices that have been idle the longest will
be kicked first. If none of the connected devices are idle,
then the priority shifts to
signal strength
.
•
Signal Strength
- Devices with the weakest signal
strength will be kicked first.
Note: If you enable this function, you should ensure that
there are multiple APs within the broadcast radius
that can accept any rejected or kicked wireless
clients; otherwise, a wireless client attempting to
connect to an overloaded NWA will be kicked
continuously and never be allowed to connect.
Apply
Click this to save your changes to the NWA.
Reset
Click this to return this screen to its last-saved settings.
Table 80
Load Balancing
FIELD
DESCRIPTION
Summary of Contents for NWA-3550
Page 2: ......
Page 8: ...Safety Warnings NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 8...
Page 10: ...Contents Overview NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 10...
Page 20: ...Table of Contents NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 20...
Page 22: ...22...
Page 40: ...Chapter 2 The Web Configurator NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 40...
Page 80: ...Chapter 3 Tutorial NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 80...
Page 82: ...82...
Page 92: ...Chapter 5 Management Mode NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 92...
Page 108: ...Chapter 6 AP Controller Mode NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 108...
Page 144: ...Chapter 8 Wireless Configuration NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 144...
Page 168: ...Chapter 10 Wireless Security Screen NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 168...
Page 182: ...Chapter 13 MAC Filter Screen NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 182...
Page 186: ...Chapter 14 IP Screen NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 186...
Page 194: ...Chapter 15 Rogue AP Detection NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 194...
Page 216: ...Chapter 17 Internal RADIUS Server NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 216...
Page 244: ...Chapter 19 Log Screens NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 244...
Page 270: ...Chapter 21 Load Balancing NWA 3160 Series User s Guide 270...
Page 274: ...Chapter 22 Dynamic Channel Selection NWA 3160 Series User s Guide 274...
Page 286: ...Chapter 23 Maintenance NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 286...
Page 287: ...287 PART III Troubleshooting and Specifications Troubleshooting 289 Product Specifications 297...
Page 288: ...288...
Page 296: ...Chapter 24 Troubleshooting NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 296...
Page 304: ...304...
Page 398: ...Appendix F Text File Based Auto Configuration NWA 3500 NWA 3550 User s Guide 398...
















































