8-
43
8
ROBOT LANGUAGE
8-5 Sample Programs
8-5-10 Palletizing for special pallets
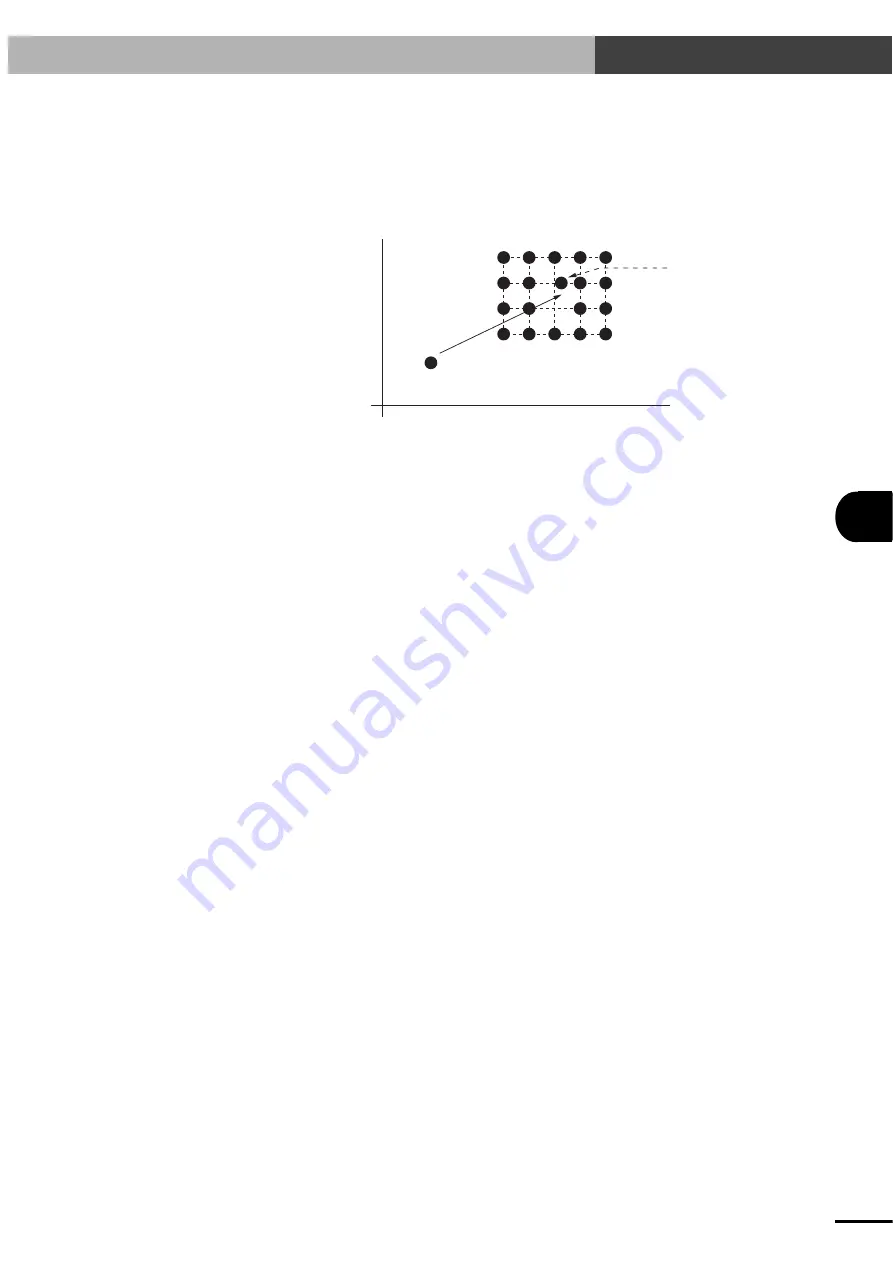
With this sample program, the robot picks up a workpiece supplied at P0 and place it sequentially on
a 4
×
5 pallet. However, the robot does not place a workpiece in the position at row 2 (from bottom),
column 3. Moreover, the position at row 3, column 3 is slightly shifted, so it should have data as a
different point (P1).
Point B (=P252)
Point C (=P253)
Point D (=P254)
Place points
Pick point
Point A (=P251)
P0
X
P1
Y
■
Teaching each point of P0, P1 and P251 to P254 should be completed beforehand in
PNT (point) mode. (Matrix is defined as pallet number 0 in this example.)
Program
Comment
[NO0]
001: MAT
4,
5,
0
; Defines 4
×
5 matrix as pallet number 0
002: C
1
; Sets counter variable to 1
003: L
0
; Label definition
004: JMPC
1,
8
; Jumps to L1 if counter variable is 8
005: MOVA
0,
100
; Moves to pick point
006: CALL
1,
1
; PICK routine call
007: JMPC
2,
13
; Jumps to L2 if counter variable is 13
008: MSEL
0
; Specifies movement matrix
009: MOVM
C,
100
; Moves to feed destination point (on pallet)
010: CALL
2,
1
; PLACE routine call
011: L
1
; Label definition
012: JMPC
3,
20
; Jumps to L3 if counter variable is 20
013: C+
; Counter variable increment
014: JMP
0,
0
; Jumps to L0
015: L
2
; Label definition
016: MOVA
1,
100
; Moves to position at row 3, column 3
017: CALL
2,
1
; PLACE routine call
018: JMP
1,
0
; Jumps to L1
019: L
3
; Label definition
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com
















































