17
Special safety instructions
p)
Do not use any attachments that require
liquid coolants.
The use of water or other
liquid coolants can lead to an electric shock.
Recoil and corresponding safety
instructions
Recoil is the sudden reaction due to a rotating
attachment (e.g. grinding wheel, grinding disc,
wire brush, etc.) snagging or blocking, Snagging
or blocking results in a sudden stoppage of the
rotating attachment. This causes an uncontrolled
electric tool to accelerate in the opposite direction
to the direction of rotation of the attachment at the
blocking point. If, for example, a grinding wheel
snags or blocks in the workpiece, that edge of the
grinding wheel entering the workpiece may snag
and cause the grinding wheel to break out or to
cause a recoil. The grinding wheel then moves
towards or away from the operator, depending on
the direction of rotation of the wheel at the blocking
point. This can also cause grinding wheels to break.
A recoil is the result of incorrect or improper use of
the electric tool. It can be avoided by taking appro-
priate precautions as described below.
a)
Hold the electric tool firmly and bring
your body and arms into a position in
which you can absorb the recoil forces.
Always use the auxiliary handle, if
fitted, in order to have the greatest
possible control over recoil forces or
reaction moments during starting.
By
taking appropriate precautions, the operator can
control the recoil and reaction forces.
b)
Never put your hands near a rotating
attachment.
The attachment can travel over
your hand in the event of a recoil.
c)
Keep your body out of the area in which
the electric tool will move in the event of
a recoil.
The recoil drives the electric tool in the
opposite direction to the movement of the grind-
ing wheel at the blocking point.
d)
Work particularly carefully in the vicin-
ity of corners and sharp edges, etc.
Prevent attachments from rebounding
from the workpiece and jamming.
The
rotating attachment tends to jam at corners or
sharp edges or if it rebounds from the workpiece.
This causes a loss of control or recoil.
e)
Do not use a chain saw blade or saw
blade with teeth.
Such attachments frequently
cause a recoil or the loss of control over the
electric tool.
Special safety precautions for grind-
ing and abrasive cut-off operations:
f)
Use only grinding wheels that are
approved for your electric tool and the
safety hoods intended for these grinding
wheels. Grinding wheels that are not
approved for the electric tool cannot be
adequately shielded and are unsafe.
g)
Offset grinding wheels must be at
-
tached so that the grinding surface is
located beneath the safety guard.
An
incorrectly attached grinding wheel protruding
beyond the edge of the safety hood cannot be
shielded adequately.
h)
The safety hood must be securely fitted
to the electric tool and adjusted for max-
imum security so that only the smallest
possible part of the grinding wheel is
open and facing towards the operator.
The safety hood helps to protect the operators
from broken pieces, from accidental contact with
the grinding wheel and from sparks that could
cause clothing to ignite.
i)
Grinding wheels may only be used for
the recommended applications.
E.g.:
never grind with the side surface of a grinding
wheel. Grinding wheels are intended for material
removal with the end of the wheel. Forces acting
on the side of these grinding wheels can cause
them to break.
j)
Always use undamaged clamping
flanges with the right size and form for
the grinding wheel used.
Suitable flanges
support the grinding wheel and thus reduce the
danger of a grinding wheel breakage. Flanges
for cut-off grinding wheels can differ from the
flanges for other grinding wheels.
k)
Do not use worn grinding wheels from
larger electric tools.
Grinding wheels for
larger electric tools are not designed for the
higher speeds of smaller electric tools and can
break.
Further special safety precautions for
cut-off wheels:
a)
Avoid blocking of the cut-off wheel or
excessive contact pressure.
Do not make
excessively deep cuts. Overloading of the cut-off
wheel increases the pressure and the susceptibil-
ity to tilting or blocking, and hence the risk of a
recoil or grinding wheel breakage.
Summary of Contents for FKWS 9-125
Page 3: ...3 I 12 13 6 2 1 4 3 7 9 8 10 11 5...
Page 4: ...12 B A C 4 III II 14 3...
Page 111: ...111 GR Adolf W rth GmbH Co KG 3 1...
Page 112: ...112 a b c d e f g...
Page 113: ...113 h i j k l m n o p a...
Page 114: ...114 b c d e f g h i j k a b...
Page 115: ...115 c d e f a a b...
Page 116: ...116 FI FI P2 FI 30 mA...
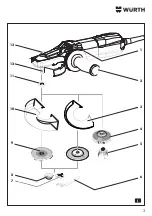
Page 118: ...118 I II 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 2 II 3 4 mm 14 3 3 13...
Page 119: ...119 8 9 6 mm 7 6 8 8 12 8 8 8 6 III 11 3 9 11 III 7 7 7 7 6 7 6...
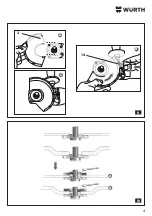
Page 120: ...120 1 1 30 40 W rth...
Page 193: ...193 BG Adolf W rth GmbH Co KG 3 1...
Page 194: ...194 a b c d e f g...
Page 195: ...195 h i j k l m n o p...
Page 196: ...196 a b c d e f g h i j a b...
Page 197: ...197 c d e f a a b...
Page 198: ...198 FI FI P2 30 mA...
Page 200: ...200 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 2 3 4 mm 14 3 3 13...
Page 201: ...201 8 9 6 mm 7 6 8 8 12 8 8 8 6 11 3 9 11 7 7 7 7 6 7 6...
Page 202: ...202 1 1 30 40 W rth...
Page 234: ...234 RU Adolf W rth GmbH Co KG 3 1...
Page 235: ...235 a b c d e f g...
Page 236: ...236 h i j k l m n o p a...
Page 237: ...237 b c d e f g h i j k a b c...
Page 238: ...238 d e f a a b...
Page 239: ...239 FI P2 30 A...
Page 241: ...241 I II 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 2 II 3 4 14 3 3...
Page 242: ...242 III 7 7 7 7 6 7 6 8 9 6 7 6 8 13 III 11 3 9 11...
Page 243: ...243 8 12 8 8 8 6 1 1 30 40...
Page 244: ...244 W rth 1 W rth masterService http www wuerth com partsmanager W rth...