G
ATEWAY
C
ONTROLLER
S
ERIES
U
SER
M
ANUAL
VALUEPOINT NETWORKS, INC. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
P
AGE
129
OF
135
4 .
T
R O U B L E
S
H O O T I N G
If you have a connectivity problem with the Controller, check the following first:
•
Make sure that the power of the Controller is on and the Ethernet cables
are connected firmly to the RJ-45 jacks.
•
Make sure the types of the Ethernet cables are correct. There are two
types—normal and crossover.
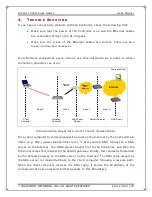
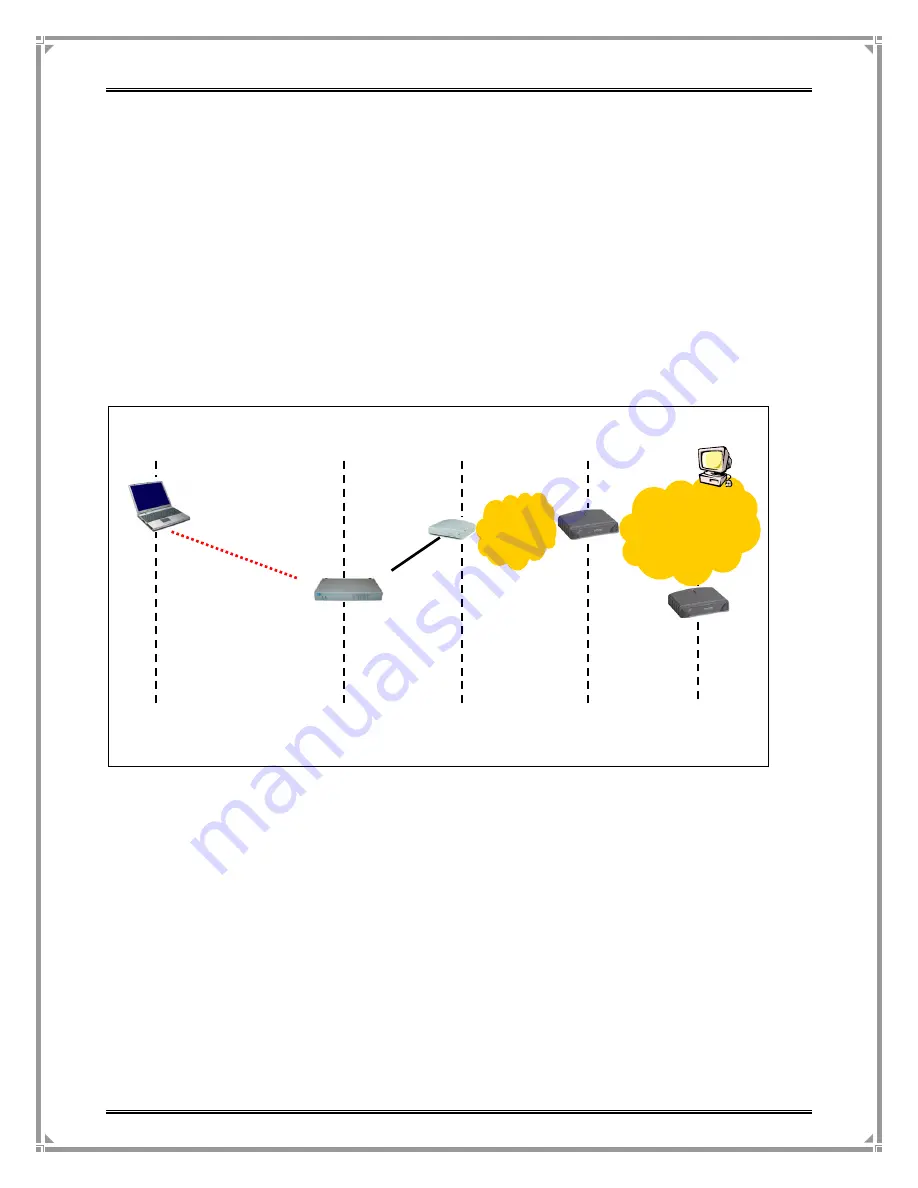
If all Network connections seem normal, use this illustration as a guide to where
connection problems can occur:
ADSL/Cable
Modem
Default Gateway
Ethernet/
RS232
Gateway
Controller
Stage A
State B
Stage C
Destination Host
Stage D
Client
Computer
DNS Server
Phone/
CAT5
Network
Internet
Communication stages for a client to reach its destination.
For a client computer to communicate with a host on the Internet by the host’s domain
name (e.g. http://www.valuepointnet.com), it first sends a DNS request to a DNS
server on the Internet. The DNS request travels first to the Controller, and then the
Controller relays this request to the default gateway. Finally, this request is forwarded
by the default gateway to the DNS server on the Internet. The DNS reply issued by
the DNS server is transmitted back to the client computer following a reverse path.
When the client computer receives the DNS reply, it knows the IP address of the
correspondent host and sends further packets to this IP address.