Functions
2.5 Distance Protection
SIPROTEC, 7SD5, Manual
C53000-G1176-C169-5, Release date 02.2011
163
2.5.3
Distance Protection with MHO Characteristic (optional)
Depending on the version ordered, the universal line protection 7SD5 can be equipped with an MHO charac-
teristic in combination with the distance protection function. If both the polygonal and the MHO characteristic
are available, they may be selected separately for phase-phase loops and phase-earth loops. The polygonal
tripping characteristic is described in Section 2.5.2.
2.5.3.1
Functional Description
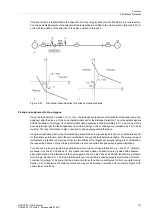
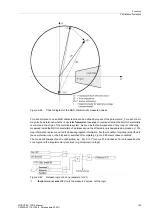
Basic characteristic
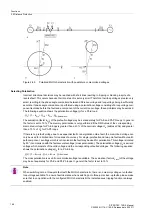
One MHO characteristic is defined for each distance zone, which represents the tripping characteristic of the
corresponding zone. In total there are six independent and one additional controlled zone for each fault imped-
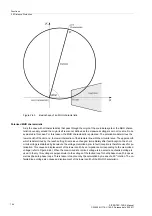
ance loop. The basic shape of an MHO characteristic is shown in Figure 2-63 as an example of a zone.
The MHO characteristic is defined by the line of its diameter which intersects the origin of the coordinate system
and the magnitude of the diameter which corresponds to the impedance Z
r
which determines the reach, and
by the angle of inclination. The angle of inclination is set in address
1511
Distance Angle
and corresponds
normally to the line angle
ϕ
Line
. A load trapezoid with the setting R
Load
and
ϕ
Load
may be used to cut the area of
the load impedance out of the characteristic. The reach Z
r
may be separately set for each zone; the inclination
angle
ϕ
Dist
as well as the load impedance parameters R
Load
, and
ϕ
Load
are common to all zones. As the char-
acteristic intersects the origin of the coordinate system, a separate directional characteristic is not required.