Functions
2.5 Distance Protection
SIPROTEC, 7SD5, Manual
C53000-G1176-C169-5, Release date 02.2011
152
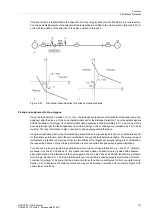
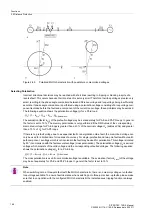
Figure 2-58
Release logic for a zone (example for Z1)
In total, the following zones are available:
Independent zones:
• 1st zone (fast tripping zone) Z1 with
X(Z1)
;
R(Z1) Ø-Ø
,
RE(Z1) Ø-E
; may be delayed by
T1-1phase
or
T1-multi-phase
,
• 2nd zone (backup zone) Z2 with
X(Z2)
;
R(Z2) Ø-Ø
,
RE(Z2) Ø-E
; may be delayed by
T2-1phase
or
T2-
multi-phase
,
• 3rd zone (backup zone) Z3 with
X(Z3)
;
R(Z3) Ø-Ø
,
RE(Z3) Ø-E
; may be delayed by
T3 DELAY
,
• 4th zone (backup zone) Z4 with
X(Z4)
;
R(Z4) Ø-Ø
,
RE(Z4) Ø-E
; may be delayed by
T4 DELAY
,
• 5th zone (backup zone) Z5 with
X(Z5)+
(forward) and
X(Z5)-
(reverse);
R(Z5) Ø-Ø
,
RE(Z5) Ø-E
, may
be delayed by
T5 DELAY
.
• 6th zone (backup zone) Z6 with
X(Z6)+
(forward) and
X(Z6)-
(reverse);
R(Z6) Ø-Ø
,
RE(Z6) Ø-E
, may
be delayed by
T6 DELAY
.
Dependent (controlled) zone:
• Overreaching zone Z1B with
X(Z1B)
;
R(Z1B) Ø-Ø
,
RE(Z1B) Ø-E
; may be delayed by
T1B-1phase
or
T1B-multi-phase
.
2.5.2.2
Setting Notes
Grading coordination chart
It is recommended to initially create a grading coordination chart for the entire galvanically interconnected
system. This diagram should reflect the line lengths with their primary reactances X in
Ω
/km. For the reach of
the distance zones, the reactances X are the deciding quantity.
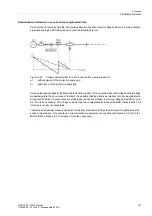
The first zone Z1 is usually set to cover 85 % of the protected line without any trip time delay (i.e. T1 = 0.00 s).
The protection clears faults in this range without additional time delay, i.e. the tripping time is the relay basic
operating time.
The tripping time of the higher zones is sequentially increased by one time grading interval. The grading margin
must take into account the circuit breaker operating time including the spread of this time, the resetting time of
the protection equipment as well as the spread of the protection delay timers. Typical values are 0.2 s to 0.4 s.
The reach is selected to cover up to approximately 80 % of the zone with the same set time delay on the short-
est neighbouring feeder (see Figure 2-59).