.
CAMERA
.
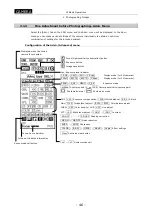
VI Basic Operations
2 Photographing Images
- 50 -
NOTE: Adjusting the focus of a dark subject can also be performed by pressing the
(focus button). When the button is right-clicked, the camera gain is
increased to adjust the exposure automatically so that the exposure time
will not be too long. Then, the live image is displayed while keeping the
exposure status. When right-clicking on the (focus button), to increase
the response at focusing, "NR OFF" status is set.
Left-click on the (focus button) to access manual mode without
adjusting the exposure.
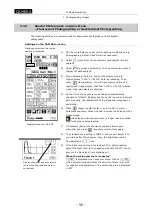
(3) Choosing photometry mode
There are two photometry modes:
Average photometry
Peak-hold photometry
Normally, average photometry should be selected. The icon indicates the currently selected
photometry mode.
Sample settings that suit different uses are described below. Try these settings before
determining your own settings.
•
There are few luminance changes over the entire screen that has a bright field
→
Average
photometry
•
Whites on the background need to be whiter.
→
Peak-hold photometry, with exposure
correction added
•
The background is mostly black, and the subject is sporadically bright.
→
Peak-hold
photometry
Selecting a photometry area
Use one of the photometry area icons to specify a range of the screen in which you want the
exposure to be adjusted.
Normally, a wide photometry range is recommended.
To avoid influences from the periphery of the screen, choose a narrow photometry range.
NOTE: Displaying phoytometry area
The photometry range is displayed with a red frame for a limited time when
the ran, right-click again.
(4) Choosing tone
When you set the tone, the contrast will change. Sample settings are shown below. Confirm
tones on the monitor when you set a tone, and select the most suitable one.
•
To observe gradation in highlight reflections
→
TONE1
Recommended example: IC chips, part-mounting circuit board solder, component leads,
gears, etc.
•
To weaken or strength the standard contrast
→
TONE2 (weak) or TONE4 (strong)
Recommended example: General photography
•
To read the difference in luminous energy from the photographed image data
→
TONE5