Section 13: Microprocessor Computer and Control –Theory of Operation
13-12
13.7.10 CPU Timing Signals
The 386EX runs from a 40 MHz crystal oscillator and the main timing is derived
from this clock. It is called CLK2. Inside the CPU, CLK2 is divided by two,
generating two new clocks, PH1 and PH2. Each T state is made up of one PH1
and one PH2 clock. There are a minimum of two T states per cycle. Each wait
state is one T state long (50 nanosecond) Therefore, adding wait states is adding
50 nanoseconds for each additional T2 states.
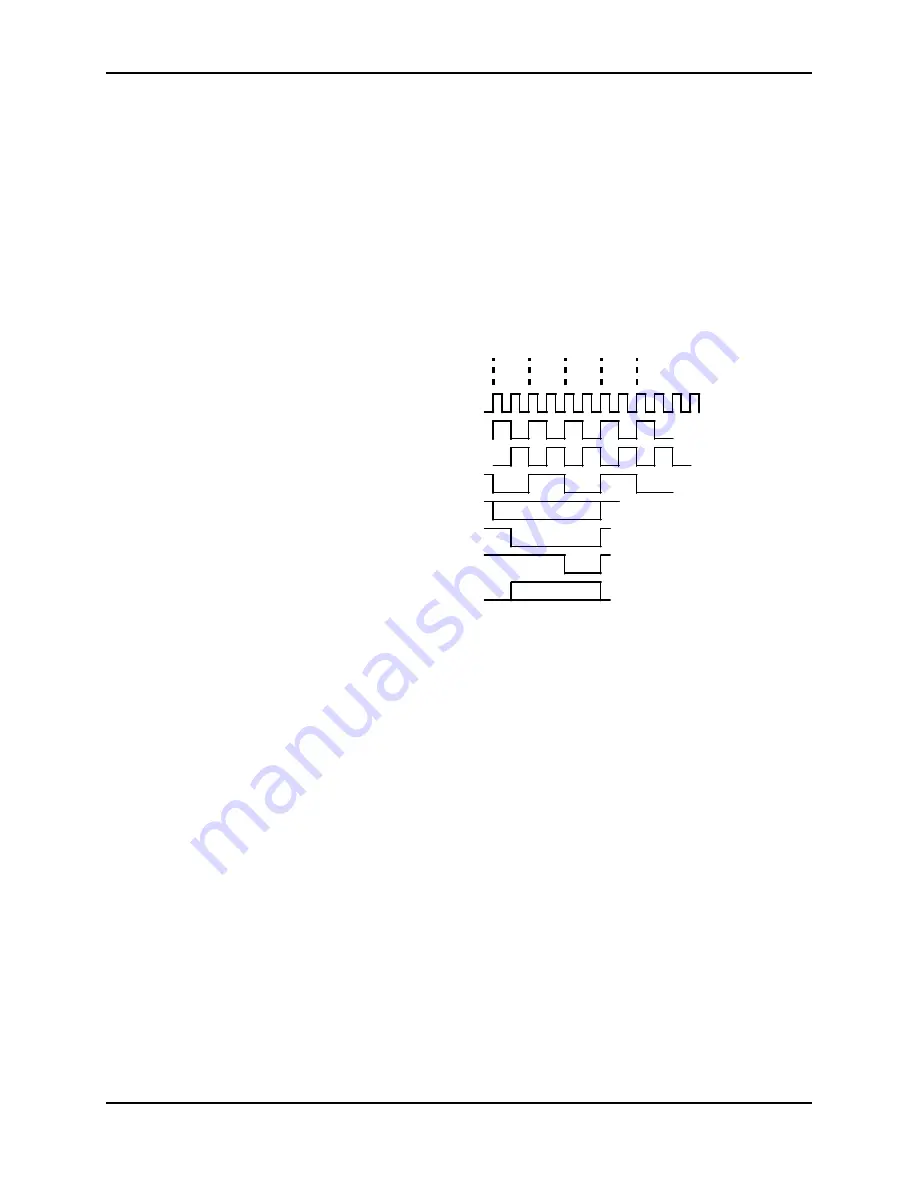
13.7.11 CPU Signals
Various signals change at various times within a cycle, and the generic timing is
shown below. Some of the key signals are ADS#, M/IO#, D/C#, W/R#, WR#,
RD#, CS0-CS6#, BLE#, and BHE#. Typical control circuits will look at ADS
#
at the end of PH2 and make decisions at this time. See Figure 13-7.
40MHZ
T1
T2
T1
T2
PH1
PH2
ADS#
W/R,BLE#,BHE#,CSO:6#,
UCS#,D/C#,M/IO,A1:25
RD#,WR#
LBA#,READY#
D0:15
Figure 13-7: CPU Signals
13.8 DRAM Control
The DRAM control consists of one 256kx16 DRAM chip, three 74ACT157
address mux chips, address resistors, and the FPGA control circuit.
The
CS6
*
(* = # = a low true signal) signal has been assigned to the DRAM
memory address space: 0-3FFFF words, or 0-7FFFF bytes. The CS6
*
control
register in the chip select unit (CSU) must be programmed for one wait state.
Since the data bus is 16 bits wide and the DRAM is a x16 part, most transfers
will be of the 16-bit variety. However, eight-bit transfers are allowed and
provisions have been made for byte addressing. This is done by using the upper
and lower cas signals, UCAS and LCAS.
13.8.1 DRAM Signals
For the DRAM design we must generate six signals, RAS#, UCAS#, LCAS#,
DRAMOE#, DRAMWR#, and CASADREN. All of these signals are generated
in the FPGA from the 386EX signals, ADS#, CS6#, M/IO#, D/C#, WR#, and
RD#.
Since the CSU is programmed for one wait state, the CSU generates the
READY
#
signal, which terminates the transfer.
Summary of Contents for NELLCOR NPB-4000
Page 66: ... THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK ...
Page 68: ...Section 7 Spare Parts 7 2 Figure 7 1 NPB 4000 C Top Assembly Drawing ...
Page 70: ...Section 7 Spare Parts 7 4 Figure 7 2 NPB 4000 C Front Case Assembly Diagram Sheet 1 of 2 ...
Page 72: ...Section 7 Spare Parts 7 6 Figure 7 3 NPB 4000 C Front Case Assembly Diagram Sheet 2 of 2 ...
Page 74: ...Section 7 Spare Parts 7 8 Figure 7 4 NPB 4000 C Rear Case Assembly Diagram Sheet 1 of 2 ...
Page 76: ...Section 7 Spare Parts 7 10 Figure 7 5 NPB 4000 C Rear Case Assembly Diagram Sheet 2 of 2 ...
Page 78: ...Section 7 Spare Parts 7 12 Figure 7 6 NPB 4000 C Power Supply Heat Sink Assembly Diagram ...
Page 80: ... THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK ...
Page 96: ... THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK ...
Page 114: ... THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK ...
Page 140: ... THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK ...
Page 180: ... THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK ...
Page 192: ... THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK ...
Page 208: ... THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK ...
Page 210: ... THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK ...
Page 211: ...Section 17 Drawings 17 3 Figure 17 1 MP 205 PCB Schematic Sheet 1 of 2 ...
Page 212: ...Section 17 Drawings 17 5 Figure 17 2 MP 205 PCB Schematic Sheet 2 of 2 ...
















































