Clarity
Matrix
Operator Manual
Page 103
18
Matrix
18.1
OVERVIEW
The encoder touch screens
Matrix
mode allows you to place fixtures on a two dimensional grid
and then display static or moving imagery on them. Therefore, the fixtures output can be
tightly integrated into a complete lighting and visual show. Clarity allows you to control and
program the imagery just like any another lighting fixture. The imagery can be displayed in
colour on RGB, RGBA and RGBW (Red, Green Blue, Amber, White) LED fixtures or in
monochrome on any fixtures that have an intensity channel.
When you patch LED arrays, Clarity automatically sub-divides them so that you can either work
with the entire array or access the individual cells. For LED types that don't have dedicated
intensity channels, virtual intensity channels are automatically created.
18.2
TERMINOLOGY
Pixel Matrix
This is the physical mapping of lighting fixtures onto a rectangular area.
Pixel Source
Each Pixel Matrix contains one or more Pixel Sources. You can add Pixel Sources to a
Pixel Matrix by clicking
New Source
.
Media
Each Pixel Source can contain one or more media files. You can add media to each Pixel
Source by selecting that Pixel Source and clicking
Add Media
.
Virtual Fixture
Clarity creates a virtual fixture for each Pixel Source.
Virtual fixtures appear in the
Selection Sidebar
in the
PixSrc
tab as
PixelSource.1
,
PixelSource.2
etc. This
allows
Clarity to treat each
Pixel Source just like a regular lighting fixture. It can be
manipulated in the programmer (media selection, size, position, shape, speed etc),
recorded into cues and it can also be controlled by Presets and Dynamics (real-time
effects).
18.3
PATCHING A LED MATRIX
In the
Patch
window, select your manufacturer/model of LED matrix and patch the appropriate
quantity to the DMX locations (addresses) that match the addresses of the fixtures.
See section
11, “Patch” for details.
18.4
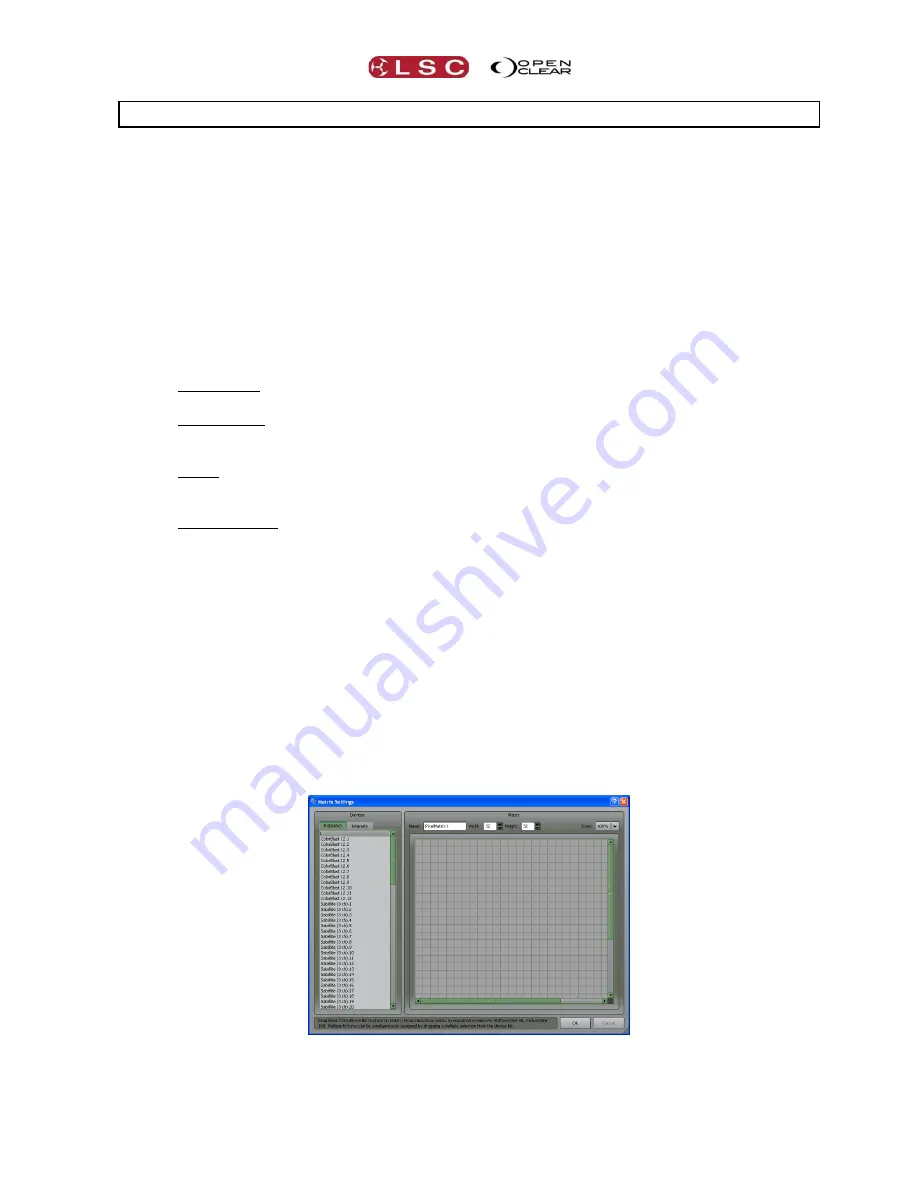
CREATING A MATRIX
In
Matrix
mode, select
New Matrix
to create a new Pixel Matrix and display the Matrix
Settings dialog box:
Use the controls at the top to select the appropriate width and height of the matrix to suit your
physical array. You can enter a descriptive name for the matrix in the
Name
box.






























