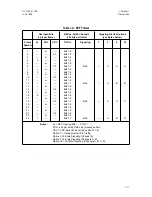
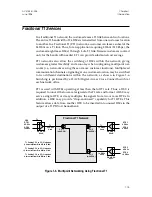
Figure 1-7. SNMP Managing Wide Area Network
SNMP Interface
Typically, there are two methods of employing SNMP to manage a network
interface device:
•
Using a Proxy Agent
which translates SNMP commands and re-
sponses back-and-forth between an SNMP-speaking client (i.e.,
SNMP manager) and a managed device which speaks another lan-
guage over its management interface. Obviously, the translation
process between SNMP and a different management language (or
protocol) is cumbersome. However, this method is sometimes cost
effective where there is already a large installed base of equipment
that does not support SNMP.
•
Using Integral SNMP
where the managed device already speaks
SNMP over its management interface. This more efficient method is
used by Access-T. In Figure 1-7, SNMP operates over Access-T’s RS232
Supervisory Ports configured for the serial link interface protocol
(SLIP) or point-to-point protocol (PPP) to carry the packetized SNMP
messages.
SNMP
Manager
Terminal Server
Terminal Server
Terminal Server
Terminal Server
Gateway
Gateway
Gateway
Gateway
T1
T1
T1
T1
Access-T
Access-T
Access-T
Access-T
T1 Network
T1 Network
RS232
(SLIP or PPP)
RS232
(SLIP or PPP)
RS232
(SLIP or PPP)
RS232
(SLIP or PPP)
LAN Segment
LAN Segment
LAN Segment
LAN Segment
DTE
DTE
DTE
DTE
DTE
DTE
ACST-0351-005
Chapter 1
June 1996
Introduction
1-17