Design Guide
195
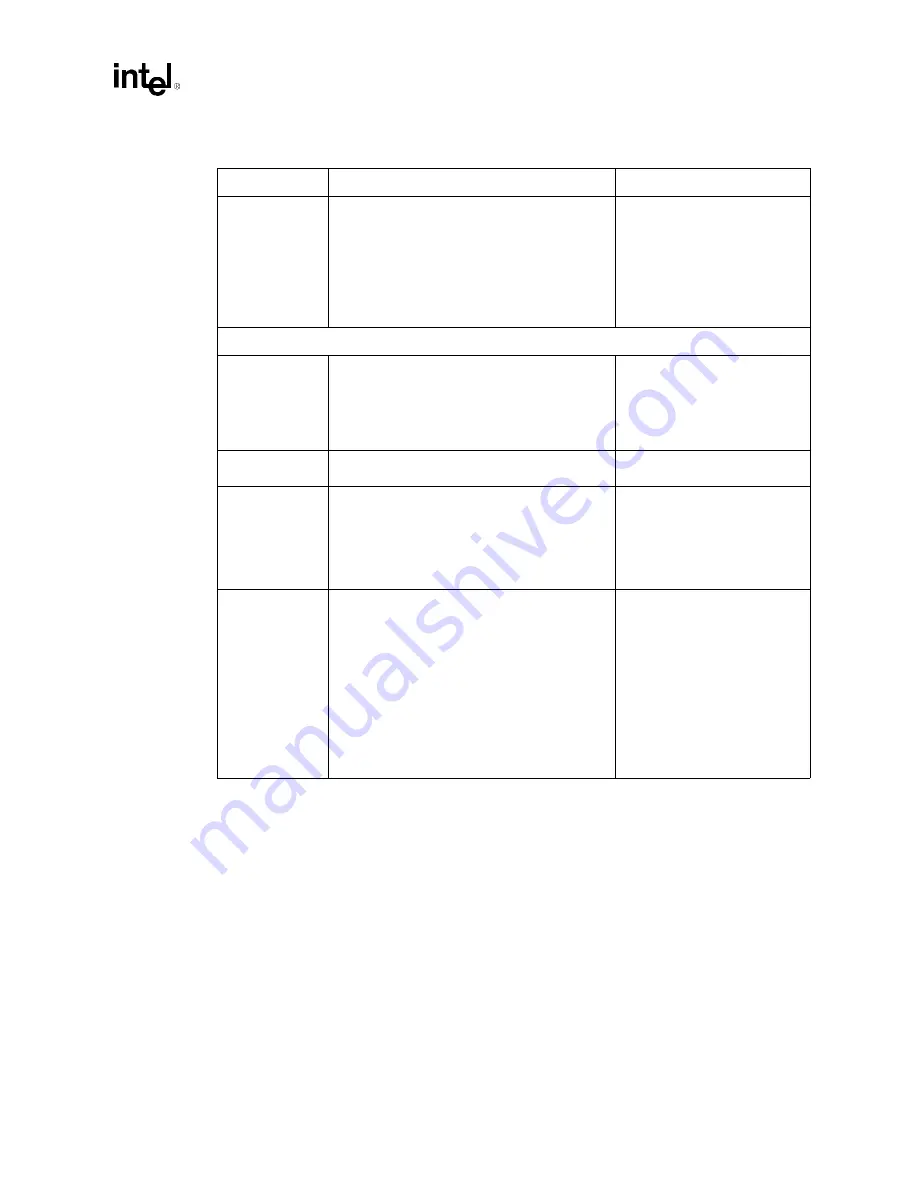
Schematic Checklist
Unused 16 bit
interfaces
•
All data and strobe signals can be left as no
connect.
•
HIVREF_[D:A] must be connected to the
reference voltage divider circuit.
•
HIVSWNG_[D:A] must be connected to the
reference voltage swing divider circuit.
•
Leave any of the HIRCOMP_[D:A] as no
connects if that hublink is not used.
•
The MCH has integration
detection logic that will detect
unpopulated 16-bit interfaces
without external pull-ups and
pull-downs.
•
Refer to
.
Voltage References – Power Planes
HDVREF[3:0]
HAVREF[1:0]
HCCVREF
•
Use one dedicated voltage divider for all these
signals.
•
Decouple the voltage divider with a 1 µF
capacitor.
•
To provide constant and clean
power delivery to the data,
address and common clock
signals of the host AGTL+
interface.
•
Refer to
VREF_DDR[5:0]
•
Decouple each signal to ground with 0.1 µF
parallel capacitor at each DIMM and MCH pin.
•
Refer to
HXSWING
HYSWING
•
The host compensation reference voltage can
be implemented using a simple voltage divider
circuit.
•
150
Ω
± 1% pull-down to ground
•
301
Ω
± 1% pull-up to VCC_CPU
•
C1 = C2 = 0.01 µF
•
The HXSWING and
HYSWING inputs of MCH are
used to provide reference
voltage for the compensation
logic.
•
Refer to
.
HISWNG_[D:A],
HIVREF[D:A]
•
MCH Hub reference swing voltage
= 0.800 V ± 5%.
•
R1 = 392
Ω
± 1%, R2 = 499
Ω
± 1%,
R3 = 453
Ω
± 1%.
•
C1= 0.1 µF, C2 = 0.01 µF.
•
•
The MCH 16-bit hub
interfaces use a
compensation voltage to
control the buffer voltage
characteristics. If multiple 16-
bit hub interfaces are used, an
HISWNG divider circuit can
be shared among the
interfaces as long as the trace
length from the divider circuit
is less than 3.5".
•
Refer to
and
NOTES:
1. The BREQ0# pin on the MCH corresponds to the BR0# pin on the processor.
2. The CPURST# pin on the MCH corresponds to the RESET# pin on the processor.
3. HA[35:3]# pins on the MCH correspond to A[35:3]# pins on the processor.
4. HD[63:0]# pins on the MCH correspond to D[63:0]# pins on the processor.
5. HADSTB[1:0]# pins on the MCH correspond to ADSTB[1:0]# pins on the processor.
6. HADSTBN[3:0]# pins on the MCH correspond to DSTBN[3:0]# pins on the processor.
7. HADSTBP[3:0]# pins on the MCH correspond to DSTBP[3:0]# pins on the processor.
8. HREQ[4:0]# pins on the MCH correspond to REQ[4:0]# pins on the processor.
9. The HTRDY# pin on the MCH corresponds to the TRDY# pin on the processor.
10.The MCH XERR# pin can be connected to the processor IERR# pin or the processor MCERR# pin.
11. In HI1.0 mode, HI_STBF and HI_STBS used to be referred as HI_STB# and HI_STB respectively.
Table 13-2. MCH Schematic Checklist (Sheet 3 of 3)
Checklist Items
Recommendations
Comments
Summary of Contents for Xeon
Page 24: ...Introduction 24 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 30: ...Component Quadrant Layout 30 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 52: ...Platform Clock Routing Guidelines 52 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 66: ...System Bus Routing Guidelines 66 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 118: ...Intel 82870P2 P64H2 118 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 146: ...I O Controller Hub 146 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 148: ...Debug Port 148 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 210: ...Schematic Checklist 210 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 220: ...Layout Checklist 220 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 222: ...Schematics 222 Design Guide This page is intentionally left blank ...
















































