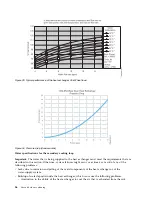
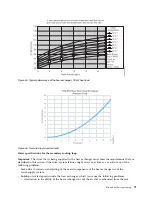
The system that supplies the cooling water must be able to measure the room dew point and
automatically adjust the water temperature accordingly. Otherwise, the water temperature must
be above the maximum dew point for that data center installation. For example, the following
minimum water temperature must be maintained:
v
18°C plus or minus 1°C (64.4°F plus or minus 1.8°F). This specification is applicable within an
ASHRAE Class 1 Environmental Specification that requires a maximum dew point of 17°C
(62.6°F).
v
22°C plus or minus 1°C (71.6°F plus or minus 1.8°F). This specification is applicable within an
ASHRAE Class 2 Environmental Specification that requires a maximum dew point of 21°C
(69.8°F).
See the ASHRAE document Thermal Guidelines for Data Processing Environments.
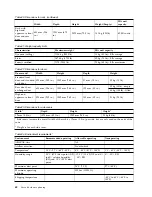
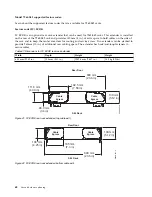
Pressure:
The water pressure in the secondary loop must be less than 690 kPa (100 psi). Normal operating
pressure at the heat exchanger must be 414 kPa (60 psi) or less.
Flow rate:
The flow rate of the water in the system must be in the range of 23 - 57 liters (6 - 15 gallons) per
minute.
Pressure drop versus flow rate for heat exchangers (including quick-connect couplings) is defined
as approximately 103 kPa (15 psi) at 57 liters (15 gallons) per minute.
Water volume limits:
The heat exchanger holds approximately 9 liters (2.4 gallons). Fifteen meters (50 ft) of 19 mm
(0.75 in.) supply and return hoses hold approximately 9.4 liters (2.5 gallons). To minimize
exposure to flooding in the case of leaks, the entire product cooling system (heat exchanger,
supply hose, and return hose), excluding any reservoir tank, must have a maximum 18.4 liters
(4.8 gallons) of water. This is a cautionary statement, not a functional requirement. Also, consider
using leak detection methods on the secondary loop that supplies water to the heat exchanger.
Air exposure:
The secondary cooling loop is a closed loop, with no continuous exposure to room air. After you
fill the loop, remove all air from the loop. An air bleed valve is provided at the top of a heat
exchanger manifold for purging all air from the system.
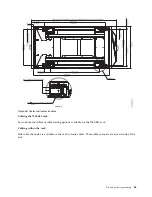
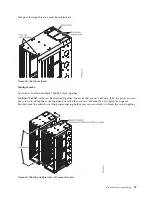
Water delivery specifications for secondary loops
Learn about the various hardware components that make up the delivery system secondary loop that
provides the chilled, conditioned water to the heat exchanger. The delivery system includes pipes, hoses,
and the required connection hardware to connect the hoses to the heat exchanger. Hose management can
be used in raised-floor and non-raised-floor environments.
The heat exchanger can remove 100% or more of the heat load from an individual rack when it is
running under optimum conditions.
The primary cooling loop is considered to be the building chilled-water supply or a modular chiller unit.
The primary loop must not be used as a direct source of coolant for the heat exchanger.
Procurement and installation of the components that are needed to create the secondary cooling loop
system are required for this design and are your responsibility. The main purpose is to provide examples
of typical methods of secondary loop setup and operating characteristics that are needed to provide an
adequate and safe supply of water to the heat exchanger.
Site and hardware planning
59
Summary of Contents for 8408-44E
Page 1: ...Power Systems Site and hardware planning IBM...
Page 2: ......
Page 3: ...Power Systems Site and hardware planning IBM...
Page 16: ...xiv Site and hardware planning...
Page 18: ...2 Site and hardware planning...
Page 22: ...6 Site and hardware planning...
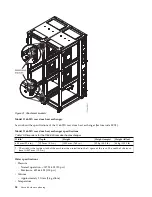
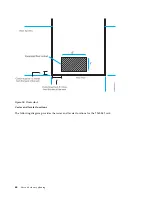
Page 51: ...Figure 19 Model 0555 and 7014 S25 plan view Site and hardware planning 35...
Page 192: ...176 Site and hardware planning...
Page 204: ...188 Site and hardware planning...
Page 205: ......
Page 206: ...IBM Printed in USA...