21
Protective Functions
*1: Reset operations acceptable 10 seconds after the trip.
*2: The inverter will not accept any reset command after an EEPROM error (E08), CPU error (E11), Ground fault (E14) or Driver error (E30) occurs with error code displayed. Turn off the inverter power once. If error is displayed when
the inverter power is turned on subsequently, the internal memory device may have failed or parameters may have not been stored correctly. In such cases, initialize the inverter, and then re-set the parameters.
*3: Reset cannot be released with the STOP/RESET key. Please reset it with the inverter power or reset terminal (18:RS).
Name
Cause(s)
Error Code
Over-current event while at constant speed
The inverter output was short-circuited, or the motor shaft is locked or has a heavy load.
These conditions cause excessive current for the inverter, so the inverter output is turned OFF.
The dual-voltage motor is wired incorrectly.
E01.
Over-current event during deceleration
E02.
Over-current event during acceleration
E03.
Over-current event during other conditions
E04.
Overload protection *
1
When a motor overload is detected by the electronic thermal function, the inverter trips and turns OFF its output.
E05.
Braking resistor overload protection
When the BRD operation rate exceeds the setting of "b090", this protective function shuts off the inverter output and displays the error code.
E06.
Over-voltage protection
When the DC bus voltage exceeds a threshold, due to regenerative energy from the motor.
E07.
EEPROM error *
2
When the built-in EEPROM memory has problems due to noise or excessive temperature, the inverter trips and turns OFF its output to the motor.
E08.
Under-voltage error
A decrease of internal DC bus voltage below a threshold results in a control circuit fault.
This condition can also generate excessive motor heat or cause low torque. The inverter trips and turns OFF its output.
E09.
Current detection error
If an error occurs in the internal current detection system, the inverter will shut off its output and display the error code.
E10.
CPU error *
2
A malfunction in the built-in CPU has occurred, so the inverter trips and turns OFF its output to the motor.
E11.
External trip
A signal on an intelligent input terminal configured as EXT has occurred. The inverter trips and turns OFF the output to the motor.
E12.
USP
When the Unattended Start Protection (USP) is enabled, an error occurred when power is applied while a Run signal is present.
The inverter trips and does not go into Run Mode until the error is cleared.
E13.
Ground fault *
2
The inverter is protected by the detection of ground faults between the inverter output and the motor upon during powerup tests.
This feature protects the inverter, and does not protect humans.
E14.
Input over-voltage
The inverter tests for input over-voltage after the inverter has been in Stop Mode for 100 seconds. If an over-voltage condition exists,
the inverter enters a fault state. After the fault is cleared, the inverter can enter Run Mode again.
E15.
Inverter thermal trip
When the inverter internal temperature is above the threshold, the thermal sensor in the inverter module detects the excessive
temperature of the power devices and trips, turning the inverter output OFF.
E21.
CPU communication error
When communication between two CPU fails, inverter trips and displays the error code.
E22.
Main circuit error *
3
The inverter will trip if the power supply establishment is not recognized because of a malfunction due to noise or damage to the main
circuit element.
E25.
Driver error *
2
An internal inverter error has occurred at the safety protection circuit between the CPU and main driver unit.
Excessive electrical noise may be the cause. The inverter has turned OFF the IGBT module output.
E30.
Thermistor
When a thermistor is connected to terminals [5] and [L] and the inverter has sensed the temperature is too high, the inverter trips and
turns OFF the output.
E35.
Braking error
When "01" has been specified for the Brake Control Enable (b120), the inverter will trip if it cannot receive the braking confirmation
signal within the Brake Wait Time for Confirmation (b124) after the output of the brake release signal.
E36.
Safe stop
Safe stop signal is given.
E37.
Low-speed overload protection
If overload occurs during the motor operation at a very low speed, the inverter will detect the overload and shut off the inverter output.
E38.
Operator connection
When the connection between inverter and operator keypad failed, inverter trips and displays the error code.
E40.
Modbus communication error
When “trip” is selected (C076=00) as a behavior in case of communication error, inverter trips when timeout happens.
E41.
EzSQ invalid instruction
The program stored in inverter memory has been destroyed, or the PRG terminal was turned on without a program downloaded to the inverter.
E43.
EzSQ nesting count error
Subroutines, if-statement, or for-next loop are nested in more than eight layers
E44.
EzSQ instruction error
Inverter found the command which cannot be executed.
E45.
EzSQ user trip (0 to 9)
When user –defined trip happens, inverter trips and displays the error code.
E50.
to
E59.
Option error
The inverter detects errors in the option board mounted in the optional slot. For details, refer to the instruction manual for the
mounted option board.
E60.
to
E69.
Encoder disconnection
If the encoder wiring is disconnected, an encoder connection error is detected, the encoder fails, or an encoder that does not support
line driver output is used, the inverter will shut off its output and display the error code shown on the right.
E80.
Excessive speed
If the motor speed rises to "maximum frequency (A004) x over-speed error detection level (P026)" or more, the inverter will shut off its
output and display the error code shown on the right.
E81.
Positioning range error
If current position exceeds the position range (P072-P073), the inverter will shut off its output and display the error code.
E83.
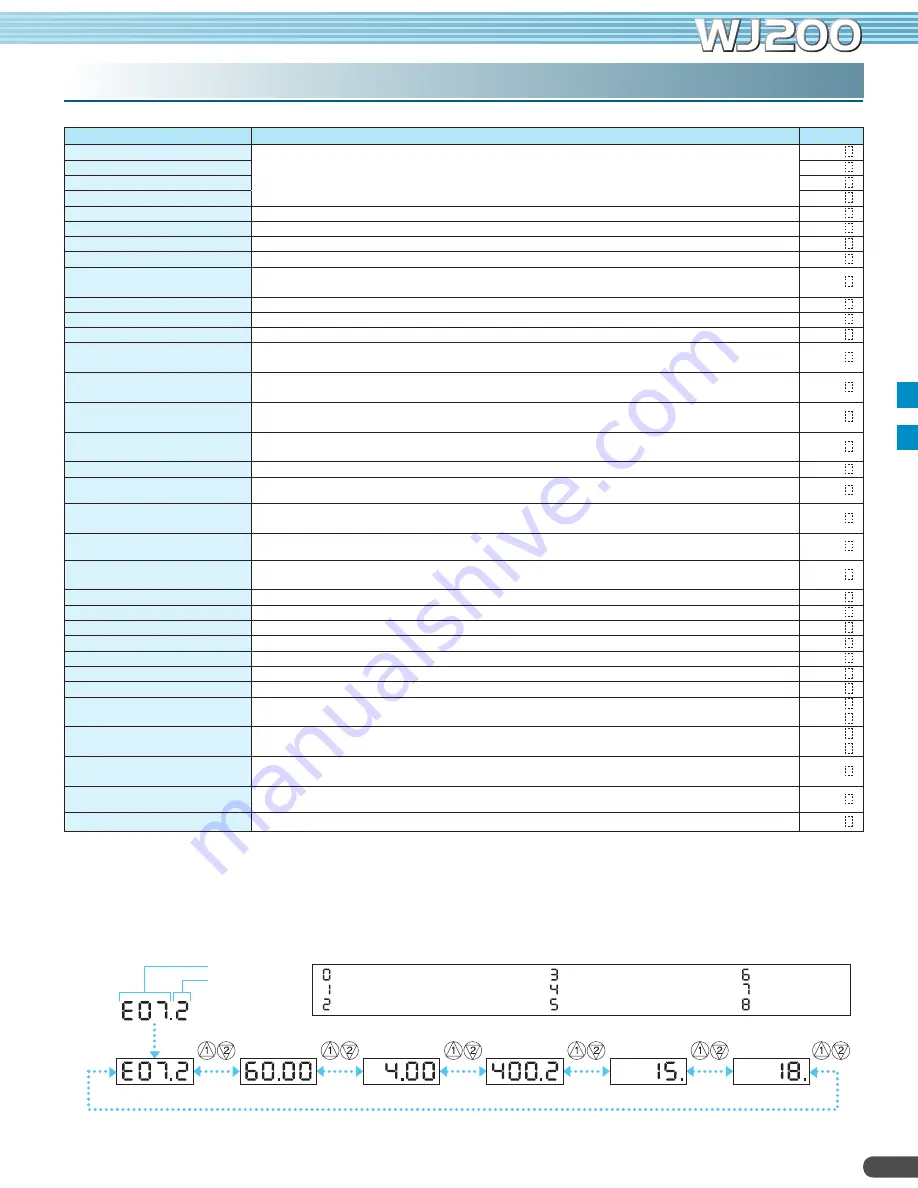
How to access the details about the present fault
Note: Indicated inverter status could be different from actual inverter behavior. (e.g. When PID operation or frequency given by analog signal, although it seems constant speed, acceleration and deceleration could be repeated in very short cycle.)
Output frequency
Output current
DC bus voltage
Elapsed RUN time
Elapsed power-ON time
: Power up or initial processing
: Stop
: Deceleration
: Constant speed
: Acceleration
: 0Hz command and RUN
: Starting
: DC braking
: Overload restriction
Trip cause
Inverter status
at trip point
Stöwer Antriebstechnik GmbH, Enneststrasse 3, 51702 Bergneustadt, tel: 02261-40970, Fax: 02261-41309








































