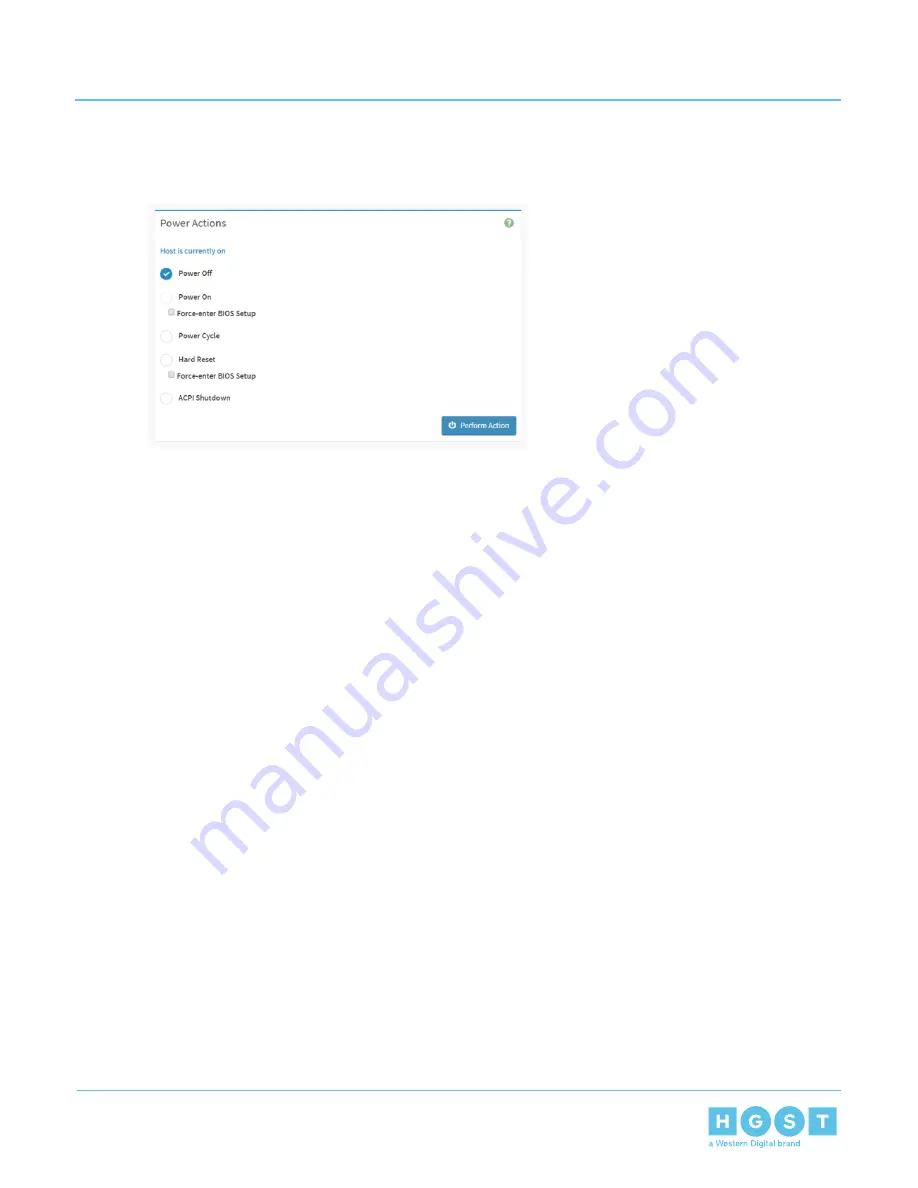
The enclosure will power off or reset and lose connection to the IP address.
Figure 283: Power Off
4.4
IPMI Overview
IPMI uses a CLI to manage and monitor the different functions of the enclosure. IPMI can access the enclosures
CPU, OS, and firmware to configuration, control, and maintain the enclosure at any moment. With the use of
IPMItool and IPMIutil, users can access the enclosure through Linux and Windows operating systems.
IPMItool is a command line interface that is used through a Linux OS for managing IPMI-enabled devices. It
uses a specific set of commands and options to interact with the enclosure. This list of commands and options
can be accessed from the Terminal by executing the command ipmitool help or they can be viewed at:
on page 213.
IPMIutil is a command line interface that is used through a Windows OS for managing IPMI-enabled devices.
It uses a specific set of commands and options to interact with the enclosure. This list of commands and
options can be accessed from the Terminal by executing the command ipmiutil -h or they can be viewed at:
on page 215.
The commands being issued within the different IPMI instances may contain instructions to add user specific
content. An example of this, using IPMItool, is seen in the following command: ipmitool –l lan –H <IP ADDRESS>
–U <USERNAME> –P <PASSWORD>. All of the instances where <>'s are used should be replaced with user
specific information.
4.4.1
Accessing IPMI on Linux
1. Download the latest version of IPMItool that supports IPMI standard version 2.0.
2. Unzip the contents of the IPMItool to the laptop being used.
3. Launch a Terminal by clicking Applications > Accessories > Terminal.
The IPMItool Terminal will appear.
4. From the Terminal, navigate to the directory where the IPMItool executable is located.
4.4.1.1
Creating a New User Using IPMItool
1. Launch a Terminal by clicking Applications > Accessories > Terminal.
The Terminal will appear.
193
4
System Management
User Guide
4.4
IPMI Overview






























