67
Common
Type ofType of
staining
illumination
filter
technique
fluorescent detection
UV
yellow or orange
Coomassie or
fluorescent
deep yellow or red
Coomassie-like dyes
(try medium-red with
Panchromatic film)
green dyes
fluorescent
red
silver
fluorescent
medium-red
PAS (glycoprotein)
fluorescent
blue or orange
Paper
A medium to hard paper with glossy finish will give best results for
black and white photographs.
Procedures for measuring the isoelectric points and molecular weights
of proteins, using calibration proteins, are described. A brief discus-
sion about evaluating PhastGel media with PhastImage is presented at
the end.
Isoelectric point measurement
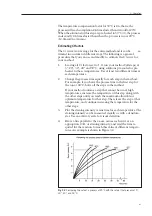
Isoelectric points (pI) of proteins are conveniently and accurately
measured using calibration proteins. Calibration proteins indicate pH
gradient profiles in gels. By measuring the distance of a sample
protein from a reference point to where it focuses, its pI can be
interpolated from the pH gradient profile.
Three pI calibration kits are available from
GE Healthcare
(Table 1). Each kit contains 8-11 proteins, depending on the kit.
Table 1:
Selecting the correct pI calibration kit for PhastGel IEF media
pI
pI range
Number of
PhastGel
calibration
covered
markers for
IEF
kit
by the kit
PhastGel interval
PhastGel
IEF4-6.5
Low pI
2.80-5.85
4 (4.15-5.85)
PhastGel IEF
5-8
High pI
5.85-10.25
4 (5.85-7.35)
PhastGel IEF
3-9
Broad pI
3.50-9.30
10 (3.50-8.65)
Procedure for pI measurement
Instructions for pI measurement in PhastGel lEF media are given
below:
1.
If you know the approximate pI of the protein of interest, select a
suitable PhastGel IEF gel. If it is unknown, use PhastGel IEF 3-9.
2.
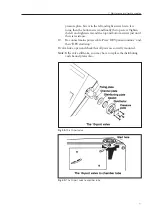
Use the appropriate separation method for IEF described in
Separation technique file No. 100, chapter 9.
6. Evaluation and presentation of data
6.2 Evaluation