59
Some development techniques may contain steps that are extremely
short and/or sensitive to temperature variations of the incoming
solutions. PhastSystem has a temperature compensation function that
can be programmed to adjust for these variations. This function is
based on the rate of development processes at 2O°C; PhastSystem uses
20°C as the reference temperature.
During a development run, deviations from 20°C are compensated for
by adjusting the programmed process time, t. If the temperature of the
solution in the development chamber is above 20°C, the process time
will be reduced. Conversely, if the temperature is below 20°C, the
process time will be extended. The degree of compensation is
determined by the temperature compensation curve, Ct curve, pro-
grammed for the method. The Ct curve is programmed with four
values, called temperature compensation factors, Ct factors.
What Ct factors are
Ct factors describe the rate of a process at a certain temperature
relative to the rate of that process at 20°C. Thus, the Ct factor for any
process run at 20°C is 1.0. Ct factors are greater than 1.0 for
temperatures above 20°C, and are less than 1.0 for temperatures
below 20°C. For example, if a method takes 30 minutes at 20°C and
15 minutes at 40°C, the Ct factor for that method at 40°C is 2.0,
that is, the rate of the process will be two times faster at 40°C than at
20°C.
Based on experimental studies of Coomassie staining with PhastGel
media, we have found that, as a general rule, the reaction rate will
double for every 20°C rise in temperature, When the Ct factors are
plotted against temperature, a Ct curve is obtained. This curve is
shown in Fig. 30.
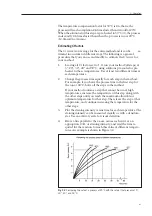
Fig. 30.
Example of a temperature compensation curve for development processes
that double in rate for every 20°C rise in temperature. The curve is made by plotting
the temperature compensation factors Ct factors. For 5°, 30°, 40°, and 50°C (20°C is
the reference temperature on which the curve is based).
5. Operation
5.8 Temperature
compensation