Garmin G900X Pilot’s Guide
190-00726-00 Rev. J
382
HAZARD AVOIDANCE
SY
STEM
O
VER
VIEW
FLIGHT
INSTRUMENTS
EIS
AUDIO P
ANEL
& CNS
FLIGHT
MANA
GEMENT
HAZARD
AV
OID
ANCE
AFCS
ADDITIONAL FEA
TURES
APPENDICES
INDEX
Displaying Precipitation weather information:
1)
Select the
MAP
Softkey (for the PFD Inset Map, select the
INSET
Softkey). This step is not necessary on the
Weather Data Link (GFDS) Page.
2)
Press the
PRECIP
Softkey.
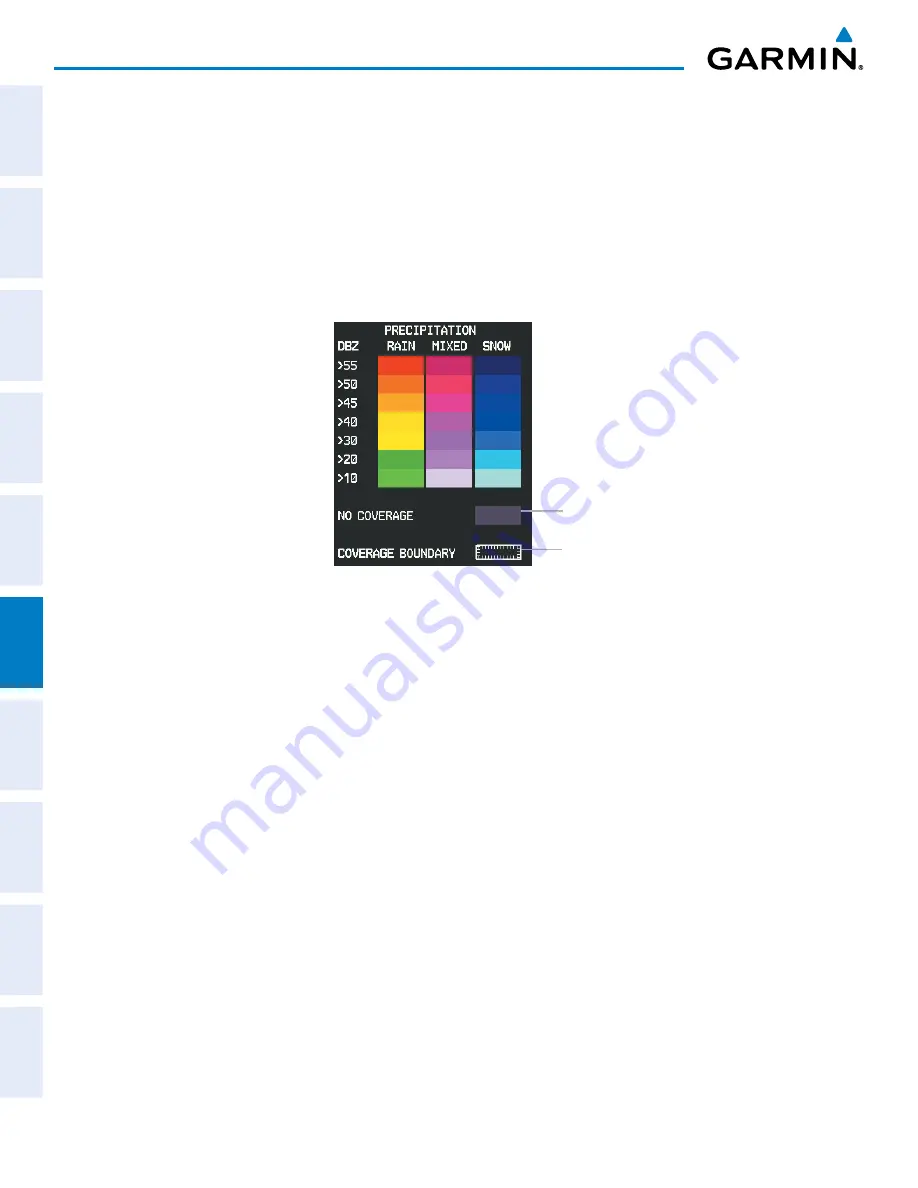
Precipitation information shown represents highest level, composite reflectivity, of radar returns. The
display of the information is color-coded to indicate the weather severity level. All weather product legends
can be viewed on the Weather Data Link (GFDS) Page. For the Precipitation legend (Figure 6-68), press the
LEGEND
Softkey when Precipitation is selected for display.
No Radar Coverage
Figure 6-68 Precipitation Weather
Product Legend
Boundary of GFDS
weather data request
The display of no radar coverage is enabled when Precipitation is selected for display. Areas where radar
coverage is not currently available or is not being collected are indicated in gray shade of purple. A white tick-
marked boundary line depicts the selected coverage area of the GFDS weather data request. This boundary
encloses the precipitation data when this weather product is displayed.
R
eflectivity
Reflectivity is the amount of transmitted power returned to the radar receiver. Colors on the Precipitation
display directly correlate to the level of detected reflectivity. Reflectivity as it relates to hazardous weather
can be very complex.
The role of radar is essentially to detect moisture in the atmosphere. Simply put, certain types of weather
reflect radar better than others. The intensity of a radar reflection is not necessarily an indication of the
weather hazard level. For instance, wet hail returns a strong radar reflection, while dry hail does not. Both
wet and dry hail can be extremely hazardous.
The different radar echo intensities are measured in decibels (dB) relative to reflectivity (Z). Weather
radars measure the reflectivity ratio, or the energy reflected
back to
the radar receiver (
designated by the
letter Z). The value of Z increases as the returned signal strength increases.






























