Syscompact 2000 M pro
Cable fault pre-location
822-175-2
69 / 98
12.5.4 Evaluating the ICM transient image
Typical ICM traces are shown below.
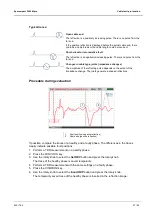
Fault is not ignited
If the fault is not ignited, the transient wave is reflected from the open cable end with opposite
polarity.
l
Cable length
t
Pulse duration
v/2 Velocity of propagation
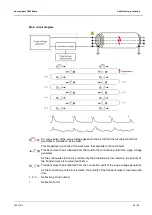
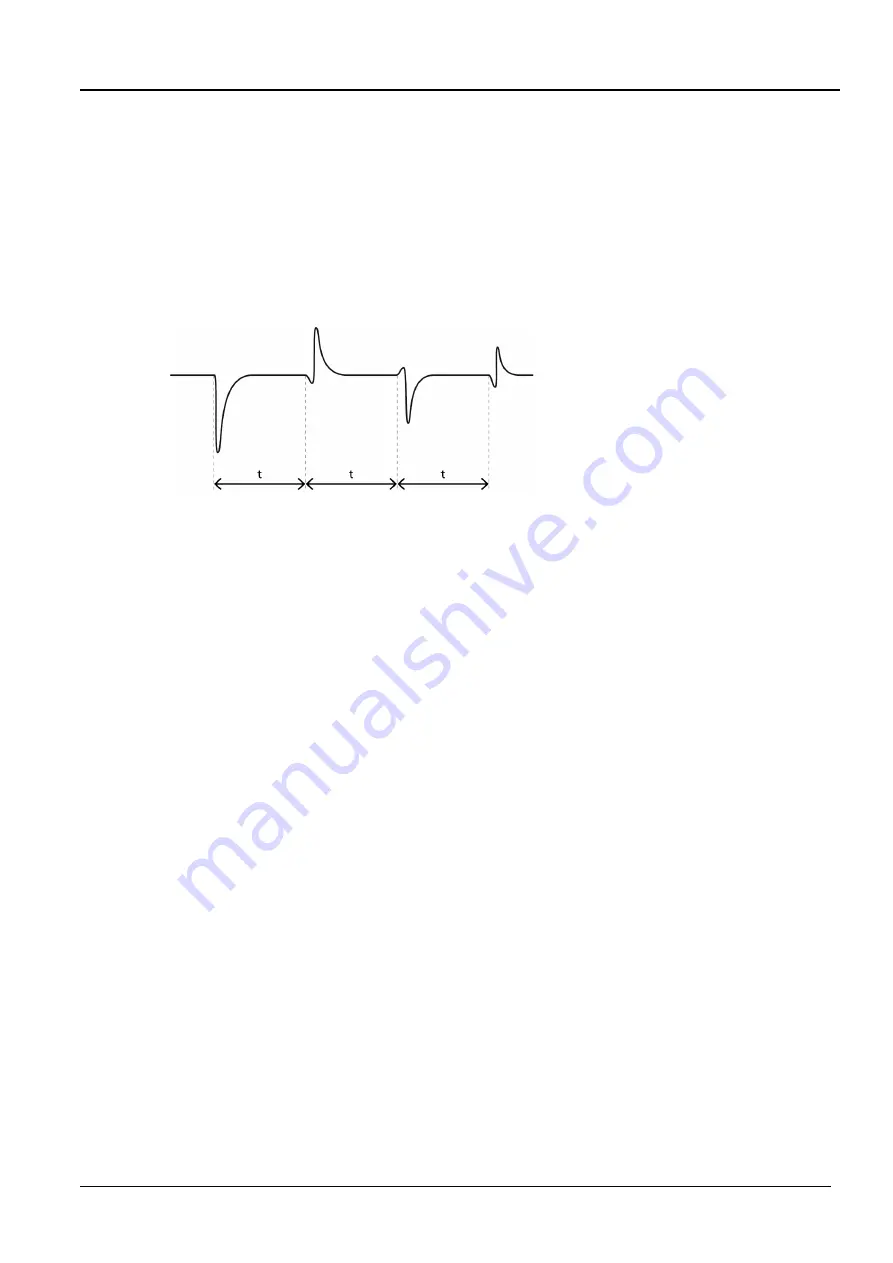
Transient image after a breakdown
The breakdown produces a travelling wave at the fault that drifts between the connection point
of the surge voltage generator and the fault with alternating polarity. The current part of the
transient wave is recorded through an inductive coupling and displayed with the help of the
time domain reflectometer. The time gap between the periodically repetitive transients is used
to calculate the fault distance to the connection point.
The first reflection contains an ignition lag (t
i
), i.e. the ionization time of the charger carrier
before a breakdown. Therefore, the second or third reflection period is included for the
evaluation. Subsequent periods are weakened by multiple reflections and can distort the
measurement result.
It can also happen that the impulse current does not generate a breakdown when the fault
occurs for the first time and is reflected back with same polarity in the direction of the fault from
the cable end. This doubles the applied voltage and leads to breakdown on the second
occurrence of the fault.
As each impedance change, such as joint or connection point, triggers reflections, they must
be considered during the evaluation. This can make it difficult to evaluate a transient image in
a branched cable.
Summary of Contents for Sys compact 2000 M pro
Page 97: ......