Temperature control
233
Goldeye G/CL Technical Manual V4.2.0
Achievable temperature difference
The cooling power and heat dissipation capability of the Goldeye is limited.
Therefore, the temperature difference (
Δ
T
) achievable by the TEC is limited as well.
However, the TEC is capable of achieving a minimum
Δ
T
in all situations.
displays the achievable
Δ
T
maintained, and the power consumption necessary to
achieve that, for each Goldeye TEC model.
The realistically achievable
Δ
T depends on the environmental conditions. It also
depends on the Peltier element and possible heat sinks and heat sources. Heat
sources are in particular the camera electronics and the Peltier element itself.
Due to changing environmental conditions, it is not always necessary for the TEC
element to maintain the maximum achievable
Δ
T. On the other hand, particular
environmental conditions allow the TEC element to achieve an even higher
Δ
T.
Note also that the TEC element cools the sensor but dissipates the removed heat
into the camera. Therefore, we can indicate a maximum power at the TEC element
that removes the heat from the camera under normal operating conditions. Above
that threshold (at more TEC power) the camera overheats due to the power
consumption of the TEC element. The value is optimally selected in a critical range.
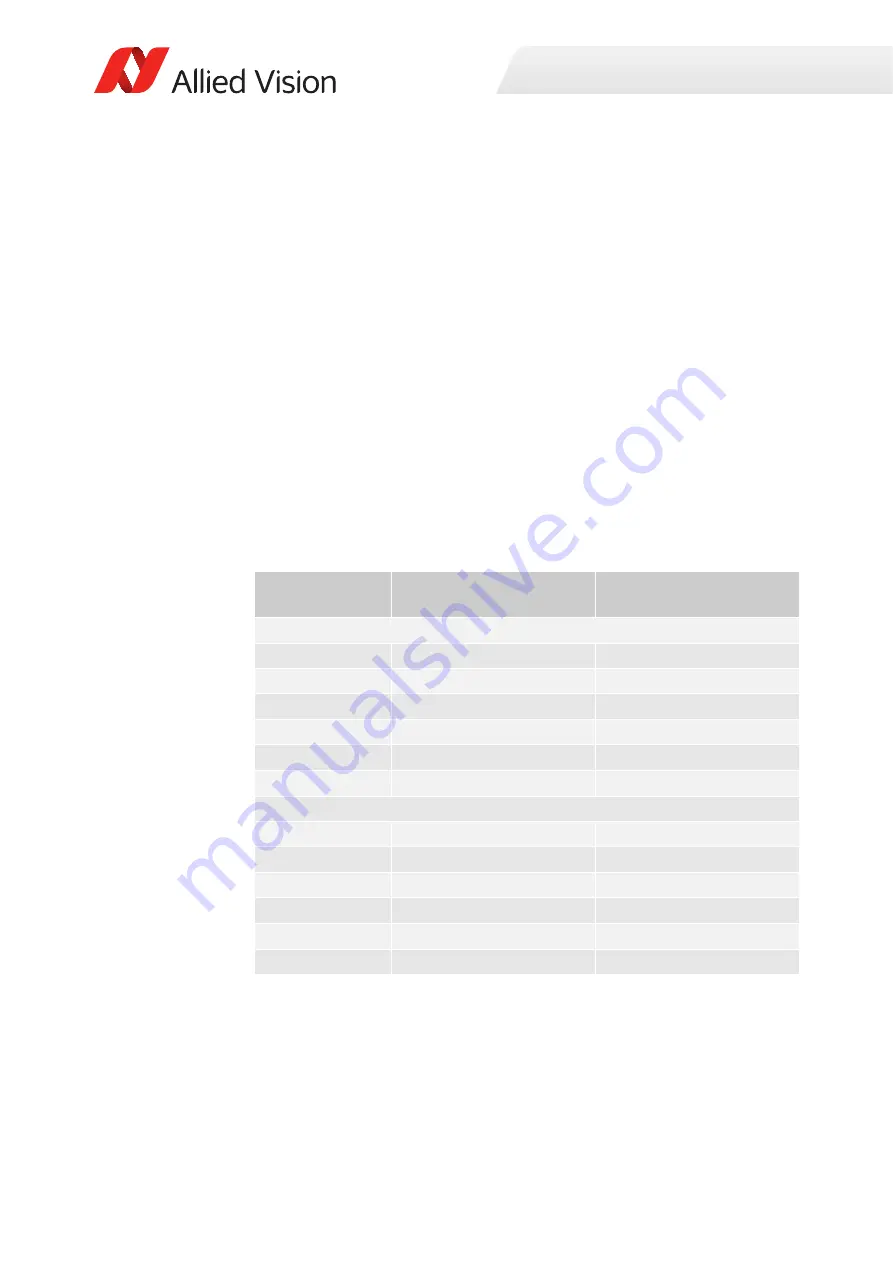
Model
Δ
T achievable between case
and FPA
Max. power to reach
Δ
T
Goldeye CL models
CL-008 TEC1
20 K
< 5.5 W
CL-008 Cool TEC1
30 K
< 5.5 W
CL-032 TEC1
30 K
< 5.5 W
CL-032 Cool TEC2
60 K
< 12 W
CL-033 TEC1
25 K
< 4 W
CL-034 TEC1
25 K
< 4 W
Goldeye G models
G-008 TEC1
20 K
< 5.5 W
G-008 Cool TEC1
30 K
< 5.5 W
G-032 TEC1
30 K
< 5.5 W
G-032 Cool TEC2
60 K
< 12 W
G-033 TEC1
25 K
< 4 W
G-034 TEC1
25 K
< 4 W
Table 143: Cooling limits for Goldeye TEC1 and TEC2 models















































