Spanning Tree Introduction: STP, RSTP, MSTP
©2008 Allied Telesis Inc. All rights reserved.
Software Version 5.2.1
AlliedWare Plus
TM
Operating System Software Reference C613-50003-00 REV E
18.7
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
RSTP uses the process described in
Table 18-1
to avoid loops.
A spanning tree running in STP mode can take up to one minute to rebuild after a topology or
configuration change. The RSTP algorithm provides for a faster recovery of connectivity
following the failure of a bridge, bridge port, or a LAN. RSTP provides rapid recovery by
including port roles in the computation of port states, and by allowing neighboring bridges to
explicitly acknowledge signals on a point-to-point link that indicate that a port wants to enter
the forwarding mode.
In rapid mode, the rapid transition of a port to the forwarding state is possible when the port is
considered to be part of a point-to-point link, or when the port is considered to be an
edge
port. An edge port is one that attaches to a LAN that has no other bridges attached.
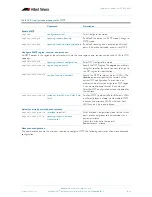
Table 18-4: RSTP port states
State
Meaning
DISABLED
STP operations are disabled on the port.
DISCARDING
The port does not participate in frame relay. The forwarding process
discards received frames and does not submit forwarded frames for
transmission.
LEARNING
The port is enabled for receiving frames only, and the learning process
can add new source address information to the forwarding database.
The port does not forward any frames.
FORWARDING
The normal state for a switch port. The forwarding process and the
Spanning Tree entity are enabled for transmit and receive operations on
the port.