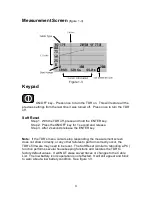
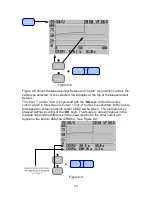
9
Zoom Key – When active, this key will zoom on Cursor 1 or Cursor 2. If
both cursors are on-screen, Zoom will center on the last Cursor key pressed (the
active Cursor). When Zoom is active use the
◄►
keys to control the zoom span.
Pressing the
◄
key will reduce the range either side of the cursor until minimum
range is reached, pressing the
►
key will expand the range either side of the
cursor until original range setting is reached. To disable the Zoom function,
press the Zoom key again. The LED will extinguish and the Measurement
Screen will return to the full range originally selected.
NOTE: Zoom function is not available when viewing saved traces
Z Scale Key – When active, this key permits control of the Z
(impedance) scale on the left side of the plot. Use the
▲▼
keys to increase or
decrease the impedance scale as required. When the impedance is reduced, the
TDR will keep the selected cable’s impedance (Z
0
) centered in the display.
Example: For a 75 Ohm coax cable if the impedance is reduced to 20 Ohms the
display scale will read 65 Ohms to 85 Ohms.
Cursor 1 & Cursor 2 Keys – These keys control the use of the
Measurement Screen cursors, one or both at the same time as follows:
Cursor 1 only – Single cursor in the display and a single CRSR1 data line
below the plot.
Cursor 2 only – Single cursor in the display and a single CRSR 2 data line
below the plot.
Cursor 1 & 2 Dual cursors in the display and two data lines below
the plot. Top data line will indicate the last cursor key
pressed (active cursor), display that cursor’s data, and is
under control of the
◄►
keys. The second data line
(CRSR
∆
) will be the difference in distance and impedance
from the opposite cursor. Both LED’s will be lit. To change
cursor control press the cursor key desired to be active.
NOTE: When the differential reading from the active cursor is from the left to the
right the differential readings will be positive. When the differential reading from
the active cursor is right to left the differential range readings will be negative.
The Z reading will rely purely on the positive or negative slope of the trace.