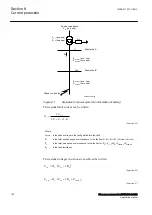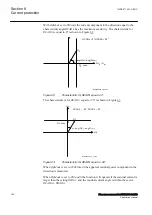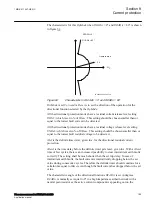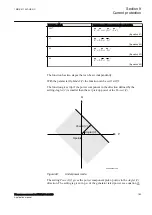
temperature is below the set value. This temperature value should be chosen below
the alarm temperature.
8.6
Directional underpower protection GUPPDUP
SEMOD156693-1 v4
8.6.1
Identification
SEMOD158941-2 v4
Function description
IEC 61850
identification
IEC 60617
identification
ANSI/IEEE C37.2
device number
Directional underpower protection
GUPPDUP
P <
2
SYMBOL-LL V2 EN-US
37
8.6.2
Application
SEMOD151283-4 v5
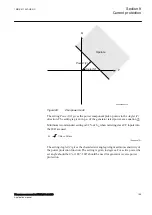
The task of a generator in a power plant is to convert mechanical energy available
as a torque on a rotating shaft to electric energy.
Sometimes, the mechanical power from a prime mover may decrease so much that
it does not cover bearing losses and ventilation losses. Then, the synchronous
generator becomes a synchronous motor and starts to take electric power from the
rest of the power system. This operating state, where individual synchronous
machines operate as motors, implies no risk for the machine itself. If the generator
under consideration is very large and if it consumes lots of electric power, it may
be desirable to disconnect it to ease the task for the rest of the power system.
Often, the motoring condition may imply that the turbine is in a very dangerous
state. The task of the reverse power protection is to protect the turbine and not to
protect the generator itself.
Steam turbines easily become overheated if the steam flow becomes too low or if
the steam ceases to flow through the turbine. Therefore, turbo-generators should
have reverse power protection. There are several contingencies that may cause
reverse power: break of a main steam pipe, damage to one or more blades in the
steam turbine or inadvertent closing of the main stop valves. In the last case, it is
highly desirable to have a reliable reverse power protection. It may prevent damage
to an otherwise undamaged plant.
During the routine shutdown of many thermal power units, the reverse power
protection gives the tripping impulse to the generator breaker (the unit breaker). By
doing so, one prevents the disconnection of the unit before the mechanical power
has become zero. Earlier disconnection would cause an acceleration of the turbine
generator at all routine shutdowns. This should have caused overspeed and high
centrifugal stresses.
Section 8
1MRK 511 407-UEN C
Current protection
160
Phasor measurement unit RES670 2.2 IEC
Application manual
Summary of Contents for Relion RES670
Page 1: ...RELION 670 SERIES Phasor measurement unit RES670 Version 2 2 IEC Application manual...
Page 2: ......
Page 46: ...40...
Page 52: ...46...
Page 92: ...86...
Page 112: ...106...
Page 178: ...172...
Page 216: ...210...
Page 232: ...226...
Page 286: ...280...
Page 328: ...322...
Page 340: ...334...
Page 380: ...374...
Page 381: ...375...