Functions
76
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
The stabilizing quantity is derived from the arithmetical sum of the absolute values of
|
I
1
| + |
I
2
|. The following definitions apply:
The differential current
I
diff
= |
I
1
+
I
2
|
and the stabilization or restraining current
I
stab
= |
I
1
| + |
I
2
|
I
diff
is derived from the fundamental frequency current and produces the tripping effect
quantity,
I
stab
counteracts this effect.
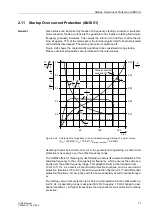
To clarify the situation, three important operating conditions with ideal and matched
measurement qualities should be examined:
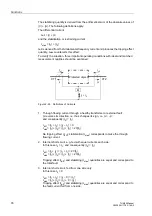
Figure 2-29
Definitions of Currents
1. Through flowing current through a healthy transformer or external fault:
I
2
reverses its direction, i.e. thus changes its sign, i.e.
I
2
= –
I
1
;
and consequently |
I
2
| = |
I
1
|
I
diff
= |
I
1
+
I
2
| = |
I
1
–
I
1
| = 0
I
stab
= |
I
1
|+ |
I
2
| = |
I
1
| + |
I
1
| = 2
⋅
|
I
1
|
No tripping effect (
I
diff
); stabilization (
I
stab
) corresponds to twice the through
flowing current.
2. Internal short-circuit, e.g. fed with equal currents each side:
In this case
I
2
=
I
1
; and consequently |
I
2
| = |
I
1
|
I
diff
= |
I
1
+
I
2
| = |
I
1
+
I
1
| = 2
⋅
|
I
1
|
I
stab
=|
I
1
|+ |
I
2
| = |
I
1
| + |
I
1
| = 2
⋅
|
I
1
|
Tripping effect (
I
diff
) and stabilizing (
I
stab
) quantities are equal and correspond to
the total fault.
3. Internal short-circuit, fed from one side only:
In this case
I
2
= 0
I
diff
= |
I
1
+
I
2
| = |
I
1
– 0| = |
I
1
|
I
stab
=|
I
1
|+ |
I
2
| = |
I
1
| + 0 = |
I
1
|
Tripping effect (
I
diff
) and stabilizing (
I
stab
) quantities are equal and correspond to
the fault current fed from one side.
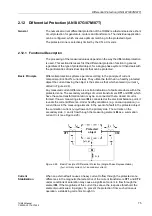
Protected object
M
CT1
CT2
I
p
1
I
p
2
I
1
+
I
2
I
1
I
2