Functions
132
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
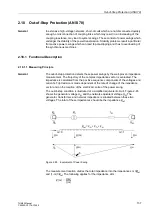
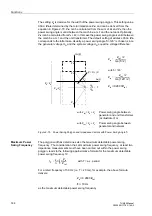
polygon P/SPOL and the trip polygon TPOL, and the rate of change
∆
Z/
∆
t are
matched to one another in such a way that power swings are reliably detected and the
desired impedance zone (Z1 or Z1 & Z2) of the impedance protection is blocked. The
blocking remains effective until the measured impedance vector has left again the trip
polygon / power swing polygon, the impedance changes faster than the change rate,
or asymmetrical power conditions rule out the possibility of a power swing. The power
swing blocking time is also limited by a parameter setting
(
Blocking of the
Impedance Stages
Power swing blocking is mostly used for impedance stage Z1, because the delay time
T1 for this stage is set low. Accordingly, a high delay time T2 must be set for zone Z2.
In the overreach zone Z1B no power swings can occur by definition, since the network
breaker is open and there is thus no second machine for power swings. Likewise, the
power swing blocking does not block the non-directional overcurrent stage (T3).
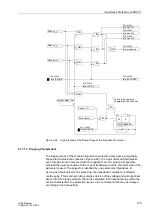
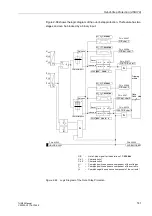
Figure 2-63 Logic Diagram for the Power Swing Blocking of the Impedance Protection
2.17.3.1 Setting Hints
The power swing blocking is only effective if address
has been
set to ON.
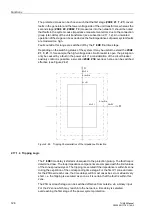
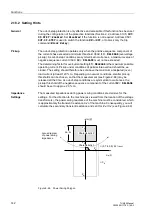
A sensible compromise has to be found for the distance between the power swing
polygon and the trip polygon (parameter:
(address
) and for the
rate of change (parameter:
(address
)). It must be kept in mind that the
rate of change is not constant and decreases with increasing proximity to the origin of
the coordinate system.The rate of change is also determined by power system condi-
tions, such as the impedance between the systems involved in the power swing, and
by the power swing frequency (see also Section 2.18 Out-of-Step Protection).
3315 dZ/dt
3314 P/SPOL-TPOL
3966
Imp. picked up
3317 T-ACTION P/S
3976
Power Swing
ON
OFF
3313 POWER SWING
"1"
I
L1
I
L3
I
L2
I2
&
3-pole pickup
I2<0,1I/In, Gen
Z(Tent)
Z(Tent-
∆
t)
Within
P/S polygon
Outside
P/S polygon
P/SPOL
OR
Release of Power
swing blocking
Rate of
change
Tent
P/SPOL
TPOL
P/SPOL
Within
Trip polygon
&
&
R
S Q
"Power swing
presumed"
&
Blocking
Z(Tent)
First value within P/S polygon
(at Tent)
Z(Tent-
∆
t) Last value outside P/S polygon
P/SPOL
Power swing polygon
TPOL
Trip polygon
∆
Z /
∆
t
Rate of change of the impedance
vector
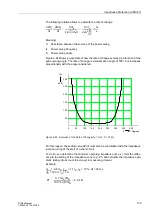
<
>
∆
Z /
∆
t
see Figure 2-61