S5-95F
Introduction to STEP 5
7
Introduction to STEP 5
This chapter explains how to program the S5-95F. It describes how to write a program, how the
program is structured, the types of blocks the program uses, and the number representation of the
STEP 5 programming language.
7.1
Writing a Program
A control program specifies a series of operations that tell the programmable controller how it has to
control a system. You must write the program in a very special language and according to specific
rules so that the programmable controller can understand it. The standard programming language
that has been developed for the SIMATIC S5 family is called STEP 5.
The S5-95F is designed for failsafe operation. That is why you can change some parameters in
safety operation only via a special data block (see section 7.3.5). In the test mode, you must not
observe this restriction.
7.1.1
Methods of Representation
The following methods of representation are possible with the STEP 5 programming language.
•
Statement List (STL)
STL represents the program as a sequence of operation mnemonics. A statement has the fol-
lowing format.
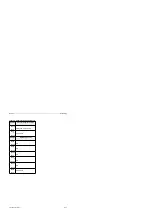
a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a
a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a
a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a
a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a
a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a
a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a
A I
0.1
Operation
Operand
Parameter
Operand ID
002:
Relative address of the statement
in a particular block
The operation tells the programmable controller what to do with the operand. The parameter in-
dicates the operand address.
•
Control System Flowchart (CSF)
CSF represents logic operations with graphics symbols.
•
Ladder Diagram (LAD)
LAD graphically represents control functions with circuit diagram symbols.
You cannot use CSF and LAD with the PG 605 and PG 615 programmers.
EWA 4NEB 812 6210-02
7-1