Application planning
6.8 Use in series connection
3VL molded-case circuit breakers
System Manual, 03/2009, 110 0110 - 02 DS 01
81
6.8
Use in series connection
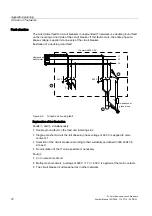
In the case of circuit breakers connected in series, the overload and short-circuit protection is
described as "selective" when, from the point of view of the energy flow, only the circuit
breaker immediately upstream of the fault switches off.
Current selectivity
The selectivity can be calculated in the overload range by comparing the current
characteristic curves and the time characteristic curves. In the short-circuit range, this
comparison leads to values that are too low. The reason for this is that the trip unit behaves
differently in the case of short-circuit currents compared to its long-term behavior, e.g. in the
case of overloads.
If the short-circuit currents differ sufficiently at the points where two circuit breakers are
mounted, the instantaneous short-circuit releases can normally be set such that if a short-
circuit occurs downstream from the circuit breaker which itself is downstream from the short-
circuit release, only the downstream one trips.
If the short-circuit currents are approximately the same at the points where the circuit
breakers are mounted, the time grading of the tripping currents of the short-circuit releases
only enables selectivitiy up to a specific short-circuit current .
This current is referred to as the selectivity limit.
If the values determined by the short-circuit current calculation (e.g. according to
DIN VDE 0102) at the mounting point of the downstream circuit breaker lie below the
selectivitiy limit listed in the respective table for the selected combination, selectivity is
guaranteed for all possible short-circuit reductions at the mounting point.
If the calculated short-circuit current at the mounting point is higher than the selectivity limit,
selective tripping by the downstream circuit breaker is only ensured up to the value listed in
the table. The configuring engineer must judge whether the value can be considered to be
sufficient because the probability of, for example, the maximum short-circuit occurring is low.
Otherwise, a circuit breaker combination should be chosen whose selectivity limit lies above
the maximum short-circuit current.
Time selectivity
Time selectivity is an alternative possibility for securing selectivity if the short-circuit currents
are approximately the same at the mounting points. To achieve this, the upstream circuit
breaker requires delayed short-circuit releases, so that if a fault occurs, only the downstream
circuit breaker will disconnect the affected part of the system from the network.
Both the tripping delays and the tripping currents of the short-circuit releases are graded.
Zone-Selective Interlocking (ZSI) has been developed by SIEMENS for the SENTRON VL
circuit breakers to prevent long, undesired release times when several circuit breakers are
connected in series.
ZSI enables the tripping delay to be reduced to a maximum of 100 ms for the circuit breaker
upstream from the location of the short-circuit.
When selecting a circuit breaker, the circuit breaker must be capable of dealing with the
initial balanced short-circuit current I
K
at the mounting point.
You can find more information in the manual "SENTRON WL and SENTRON VL
(PROFIBUS) circuit breakers with communication capability (PROFIBUS)" (Order
No. A5E01051347-01).
Содержание SENTRON 3VL series
Страница 2: ......
Страница 10: ...Table of contents 3VL molded case circuit breakers 10 System Manual 03 2009 110 0110 02 DS 01 ...
Страница 40: ...System overview 4 2 Key data 3VL molded case circuit breakers 40 System Manual 03 2009 110 0110 02 DS 01 ...
Страница 350: ...Correction sheet 3VL molded case circuit breakers 350 System Manual 03 2009 110 0110 02 DS 01 ...
Страница 358: ...Glossary 3VL molded case circuit breakers 358 System Manual 03 2009 110 0110 02 DS 01 ...
Страница 359: ......