EE Pro for TI-89.,92Plus
Analysis - AC Circuits
11
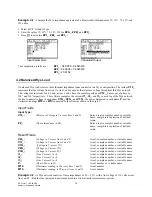
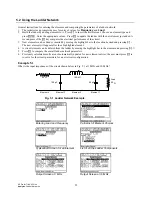
Example 3.1
Compute the impedance of a series RLC circuit consisting of a 10 ohm resistor, a 1.5 Henry inductor and a 4.7 Farad
capacitor at a frequency of 100 Hertz.
Input Screen
Output Screen
1. Choose Series for
Config
and RLC for
Elements
using the procedure described above.
2. Enter 100 for
Freq.
3. Enter 10 for
R
, 1.5 for
L
, and 4.7 for
C
.
4. Press
„
to calculate
ZZ_
and
YY_
.
5. The output screen shows the results of computation.
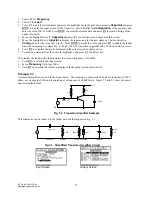
3.2 Voltage Divider
This section demonstrates how to calculate the voltage drop across a load
connected to an ideal voltage source. The load consists of impedances or
admittances in series. The software computes the current through the load and the
voltage across each impedance/admittance.
Field Descriptions
Impedance/Admittance loads in series
Load Type:
(Type of Load)
Press
¸
to display the choices; Impedance (Z) or Admittance (Y).
The choice made determines whether the third field is
ZZ_
(impedance
chain) or
YY_
(admittance chain) is displayed .
Vs_
:
(Source Voltage in V)
Enter a real or complex number, variable name, or algebraic expression
of defined terms.
ZZ_
:
(Impedances in Series)
Enter a list of real or complex numbers, or algebraic expression of
defined terms.
YY_
:
(Admittances in Series)
Enter a list of real or complex numbers, or algebraic expression
of defined terms.
IL_
:
(Load Current in A)
Returns a real or complex number, variable name or algebraic
expression.
V_
:
(Element Voltages in V)
Returns a list of real or complex numbers, variable names, or algebraic
expressions.
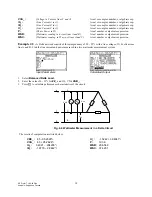
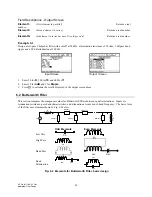
Example 3.2
Calculate the voltage drop across a series of loads connected to a voltage source of (110+25*i) volts. The load
consists of a 50 ohm resistor, and impedances of (75+22*i), and (125-40*i) ohms.
Input Screen
Output Screen
Vs
Y1
Y2
Y3
Vs
Z1
Z2
Z3