EE PRO for TI -89, 92 Plus
Equations - RL and RC Circuits
44
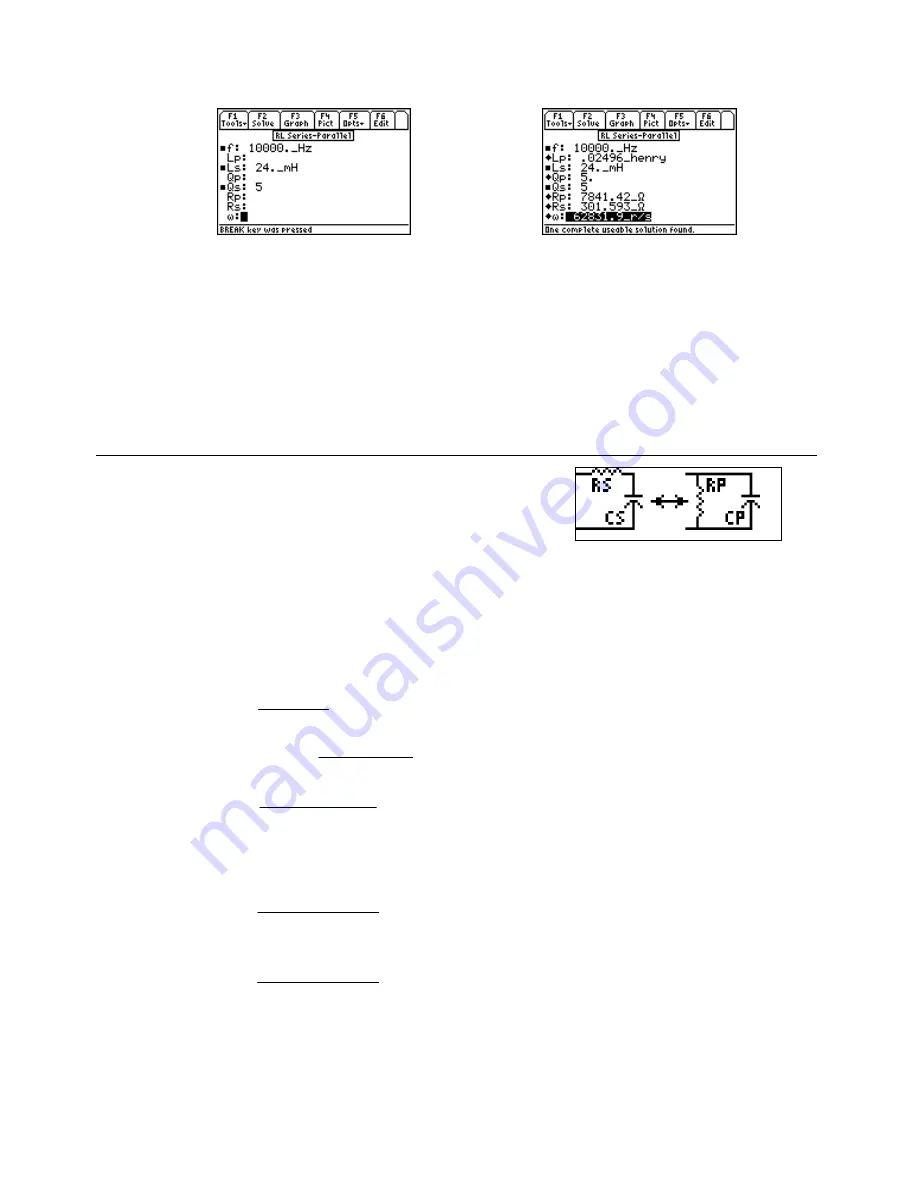
Entered Values
Calculated Results
Solution -
Upon examining the problem, the first six equations need to be solved as a set. Select these
equations, and press
„
to display the input screen enter all the known variables and press
„
to solve.
The computed results are shown in the screen display shown here.
-PQYP8CTKCDNGU.U
AO*
3U
H
A*\
%QORWVGF4GUWNVU.R
A*
4U
A
Ω
4R
A
Ω
ω
ω
TU
21.6 RC Series to Parallel
The equations in this topic show the equivalence between a series RC
circuit (Rs and Cs) and its parallel equivalent circuit with values Rp, and
Cp. The first equation converts frequency, f, to its radian equivalent
radian frequency,
ω
. The second equation computes the quality factor
Qs in terms of
ω
, Rs and Cs. The next two equations compute the parallel equivalent values as a function of Rs, Cs
and
ω
. The fifth equation defines Qp in terms of Rp, Cp and
ω
. The sixth and seventh equations compute Rs and
Cs in terms of Rp, Cp and
ω
. The last four equations describe the relationships between Rs, Cs, Rp, Cp, Qs and
Qp in a symmetrical and complementary form.
ω
π
= ⋅ ⋅
2
f
Eq. 21.6.1
Qs
Rs Cs
=
⋅ ⋅
1
ω
Eq. 21.6.2
Rp
Rs
Rs Cs
=
⋅ +
⋅
⋅
F
HG
I
KJ
1
1
2
2
2
ω
Eq. 21.6.3
Cp
Cs
Cs
Rs
=
+
⋅
⋅
1
2
2
2
ω
Eq. 21.6.4
Qp
Rp Cp
= ⋅
⋅
ω
Eq. 21.6.5
Rs
Rp
Rp
Cp
=
+
⋅
⋅
1
2
2
2
ω
Eq. 21.6.6
Cs
Rp
Cp
Rp
Cp
= +
⋅
⋅
⋅
⋅
1
2
2
2
2
2
ω
ω
Eq. 21.6.7
Rp
Rs
Qs
=
⋅ +
1
2
c
h
Eq. 21.6.8






























