EE PRO for TI - 89, 92 Plus
Equations - Transformers
122
V
V
N
N
1
2
1
2
=
Eq. 30.1.1
I
N
I
N
1
1
2
2
⋅
=
⋅
Eq. 30.1.2
V
I
V
I
1 1
2
2
⋅ =
⋅
Eq. 30.1.3
Zin
N
N
ZL
=
F
HG
I
KJ
⋅
1
2
2
Eq. 30.1.4
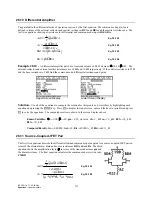
Example 30.1 -
An ideal transformer has 10 primary turns and 36 secondary turns. The primary side draws 500
mA when subjected to a 110 V input. If the load impedance is 175
Ω
, find the input impedance at the primary side
of the transformer in addition to the voltage and current on the secondary end.
Entered Values
Calculated Results
Solution -
Use all of the equations to solve this problem. Press
„
to display the input screen, enter all
the known variables and press
„
to solve the equation set. The computed results are shown in the screen
display above.
-PQYP8CTKCDNGU
+
AO#
0
0
8
A8
<.
A
Ω
%QORWVGF4GUWNVU
+
A#
8
A8
<KP
A
Ω
30.2 Linear Equivalent Circuit
The first two equations define the primary voltage and current V1 and I1 in terms of V2 and I2. The last two
equations expand the equivalent resistance Rin and reactance Xin at the primary terminals in terms of the primary
winding resistance RR1, secondary winding resistance RR2, load resistance Rl, reactances XX1 and XX2 and load
reactance Xl.
V
N
N
V
1
1
2
2
=
F
HG
I
KJ
⋅
Eq. 30.2.1
I
I
N
N
1
2
2
1
=
⋅
Eq. 30.2.2
Rin
RR
N
N
RR
Rl
=
+
F
HG
I
KJ
⋅
+
1
1
2
2
2
b
g
Eq. 30.2.3