Glossary
Roadster & Mirage S+/HD User Manual
A-5
020-100002-04 Rev. 1 (12-2008)
A video output format of some video tape and disk players. There are two types of
NTSC (National Television Standards Committee) video: NTSC 3.58 and NTSC
4.43. NTSC 3.58 is used primarily in North America and Japan. NTSC 4.43 is less
commonly used.
A type of rear-projection screen which re-directs light through the screen to increase
image brightness in front of the screen. Screen gain is usually greater than 1 but
audience viewing angles are reduced.
PAL (Phase Alternating Line) video is a 50 Hz standard with 768 x 576 resolution. It
is found on some video tape and disk players (used primarily in Europe, China and
some South American and African countries).
The smallest discernible element of data from a computer-generated image.
The phase of the pixel sampling clock relative to incoming data.
The frequency of the pixel sampling clock, indicated by the number of pixels per
line.
The projector is at presentation level when an image from a source is displayed
without the presence of a slidebar, menu, pull-down list, or error message.
The distance between the projector’s front feet centers and the screen. Also called
“Throw Distance”.
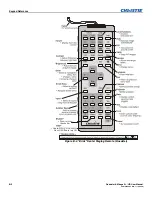
The type of code format called “A” or “B” utilized by the remote keypad(s). The
default protocol set at manufacture is Protocol “A”. By using two different keypad
protocols, adjacent projectors can be controlled independently with their remote IR
keypads.
A selectable menu item that unfolds into a list of options pertaining to it.
A manufacturer of a digital video recorder/player/server, QuBit, frequently used for
providing digital cinema data. QuVis image compression uses a proprietary
technology called Quality Priority Encoding, based on
wavelets
, in which the user
selects a quality level based on
signal-to-noise ratio
. The data rate varies to
efficiently maintain that quality level. Frames are coded individually.
A translucent panel for screen projection. Incident light travels through the incident
surface of a rear screen and forms an image on the other surface.
The ability to manipulate through software commands the physical size, placement
and/or aspect ratio of an image.
The maximum number of alternate white and black horizontal lines that can be
distinguished on a screen when a photographic target is placed between the lens and a
light source and illuminated by that source.
The maximum number of pixels that the projector can display horizontally and
vertically across an image, such as 1024 x 768 (called XGA).
The minimum time required for a CRT projector to move the position of the scanning
spot from the right edge to the left edge.
NTSC
Video
Optical Screen
PAL
Video
Pixel
Pixel
Phase
Pixel
Tracking
Presentation
Level
Projector-to-Screen
Distance
Protocol
Pull-down
List
QuVis
Rear
Screen
Resizing
Resolution
(lens)
Resolution
(projector)
Retrace
Time
(Horizontal)