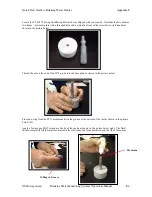
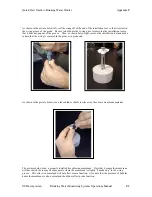
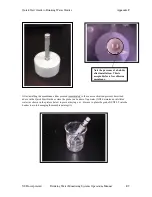
Specifications Appendix
E
YSI Incorporated Drinking Water Monitoring Systems Operations Manual
E-2
Internal logging
memory size:
384 kilobytes (150,000 individual parameter readings)
Power:
8 AA-size Alkaline Batteries or External 12 VDC
Battery Life:
Approximately 30 days at 20
°
C at 15 minute logging intervals, a 40 second DO
warm up time and turbidity, chlorophyll, or rhodamine-WT active
SENSOR
SENSOR
SENSOR
SENSOR SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
The following are typical performance specifications for each sensor. Specifications do not include drift.
Temperature
Sensor Type...........Thermistor
Range.....................-5 to 45
°
C
Accuracy................+/- 0.15
°
C
Resolution..............0.01
°
C
Conductivity
*
Sensor Type...........4 electrode cell with autoranging
Range.....................0 to 100 mS/cm
Accuracy................+/- 0.5% of r 0.001 mS/cm
Resolution..............0.001 mS/cm to 0.1 mS/cm (range dependent)
Free Chlorine, mg/L
Sensor Type.......... Rapid Pulse - Clark type, polarographic
Range.....................0 to 3 mg/L
Accuracy............... +/- 15 % of the reading or 0.05 mg/L, whichever is greater; to maintain accuracy
specification, flow must be at least 500 mL/min and pH should not change by more than
+/- 0.3 units if the mean pH is greater than 8.5.
Resolution..............0.01 mg/L
Salinity
Sensor Type............Calculated from conductivity and temperature
Range......................0 to 70 ppt
Accuracy.................+/- 1.0% of reading or 0.1 ppt, whichever is greater
Resolution...............0.01 ppt
pH
Sensor Type...........Glass combination electrode
Range.....................0 to 14 units
Accuracy................+/- 0.2 units
Resolution..............0.01 units
Depth……………200 meters
ORP
Sensor type............ Platinum button
Range.....................-999 to +999 mV
Accuracy................+/-20 mV
* Report outputs of specific conductance (conductivity corrected to 25 C), resistivity, and total dissolved solids are also
provided. These values are automatically calculated from conductivity according to algorithms found in
Standard
Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater
(Ed 1989).