ELECTRICAL AND ECU
Battery Components and Functions
12/05
6LY3 Service Manual
12-5
© 2007 Yanmar Marine International
4. If the difference in the specific gravity among
the cells of the battery is ± 0.01, the battery is
OK.
5. Measure the temperature of the electrolyte.
Since the specific gravity changes with the
temperature, 20°C (68°F) is used as the
reference temperature.
Voltage Test
Using a battery tester, the amount of discharge can
be determined by measuring the voltage drop
which occurs while the battery is being discharged
with a large current.
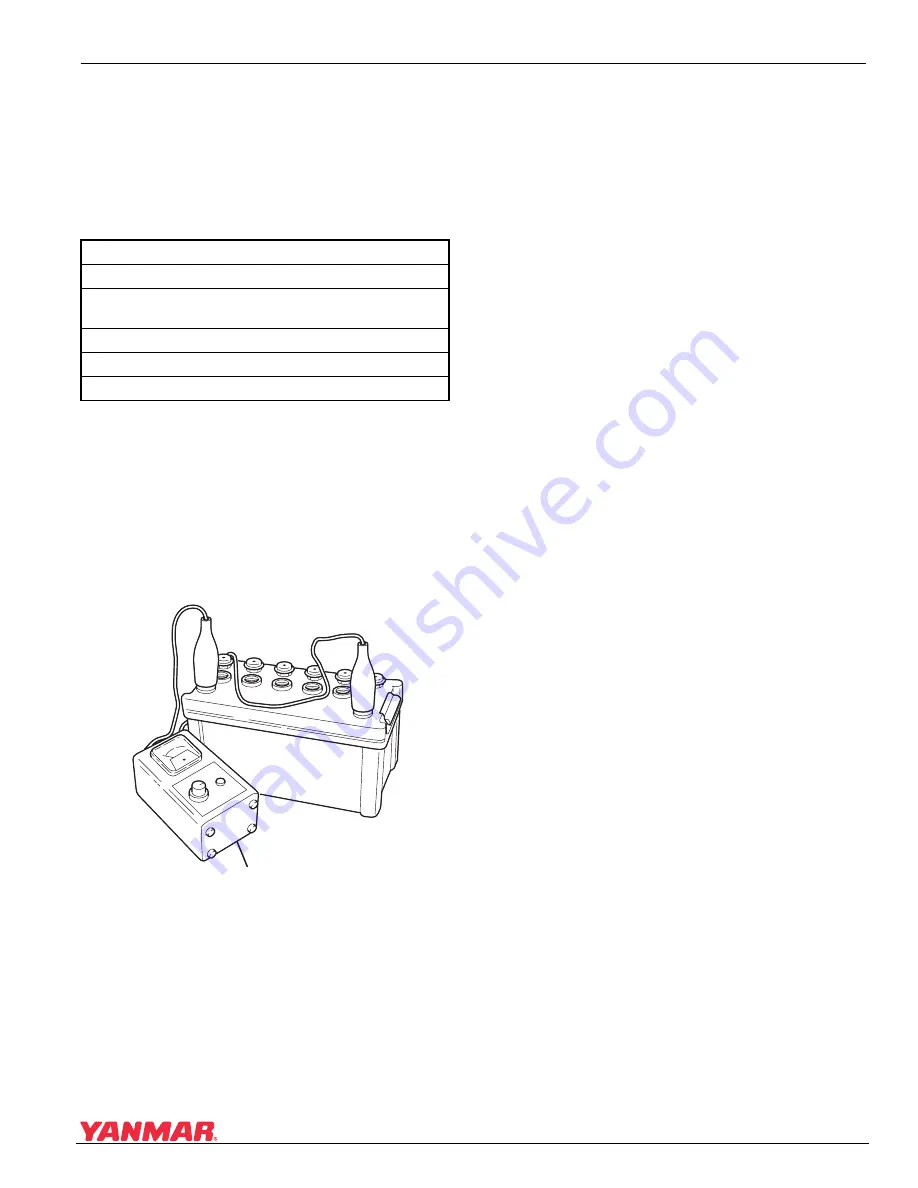
1. Connect the tester to the battery.
Use a 12V battery tester
(Figure 12-6, (1))
.
Adjust the current.
Figure 12-6
Figure 12-6
1 – 12V Battery Tester
2. Connect the positive (+) lead of the tester to the
positive (+) battery terminal, and the negative
(-) tester lead to the negative (-) battery
terminal.
3. Push the TEST button, wait 5 seconds and read
the meter.
NOTICE: Repeat the test twice to make sure the
meter indication remains the same.
Washing the Battery
1. Wash the outside of the battery with a brush
while running water over the battery. (Make
sure no water gets into the battery.)
2. If the terminals, or other metal parts, are
corroded due to exposure to electrolyte
leakage, wash off all of the acid.
3. Check the vent holes of the caps and clean if
clogged.
4. After washing the battery, dry it with
compressed air, connect the battery cable and
coat the terminals with the grease.
NOTICE: NEVER coat the terminals before
connecting the cables, the grease will act as an
insulator.
Charging the Battery
Charging Methods
There are two methods for charging a battery:
normal and rapid. Rapid charging should only be
used in emergencies.
Normal Charging
Normal charging should be conducted at a current
of 1/10 or less of the indicated battery capacity
(10A or less for a 100Ah battery).
Rapid Charging
Rapid charging is conducted over a short period of
time at a current of 1/5 to 1/2 the indicated battery
capacity (20A to 50A for a 100Ah battery).
NOTICE: Rapid charging can increase the
electrolyte temperature. Exercise care when rapid
charging the battery.
Reading the Specific Gravity at 20°C (68°F)
S
20
= St + 0.0007(t-20)
S
20
: Specific gravity at the standard temperature of 20°C
(68°F)
St: Specific gravity of the electrolyte at 20°C (68°F)
0.0007: Specific gravity change per 1°C (33.8°F)
t: Temperature of the electrolyte
(1)
0006265
















































