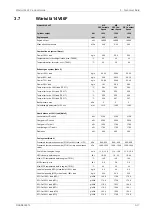
DE
DE Constant
Speed
ME
CPP Con-
stant Speed
ME
CPP Variable
Speed
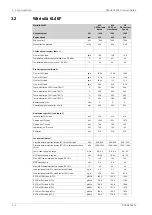
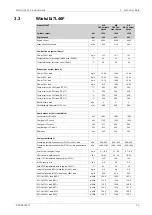
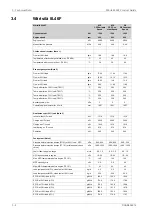
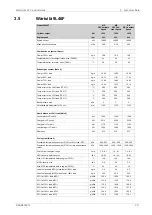
Wärtsilä 7L46F
1200
1200
1200
kW
Cylinder output
600
600
600
rpm
Engine speed
188.8
186.9
181.1
g/kWh
SFOC at 75% load (LFO)
197.9
192.2
183.1
g/kWh
SFOC at 50% load (LFO)
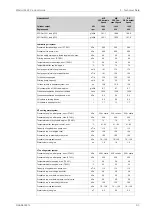
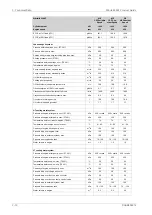
Lubricating oil system
500
500
500
kPa
Pressure before bearings, nom. (PT 201)
800
800
800
kPa
Pressure after pump, max.
40
40
40
kPa
Suction ability main pump, including pipe loss, max.
80
80
80
kPa
Priming pressure, nom. (PT 201)
56
56
56
°C
Temperature before bearings, nom. (TE 201)
75
75
75
°C
Temperature after engine, approx.
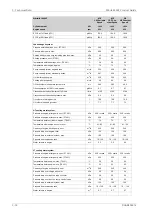
191
191
207
m
3
/h
Pump capacity (main), engine driven
179
179
207
m
3
/h
Pump capacity (main), electrically driven
150
150
150
m
3
/h
Oil flow through engine
45
45
45
m
3
/h
Priming pump capacity
15.0
15.0
15.0
m
3
Oil tank volume in separate system, min
0.7
0.7
0.7
g/kWh
Oil consumption at 100% load, approx.
1600
1600
1600
l/min
Crankcase ventilation flow rate at full load
0.4
0.4
0.4
kPa
Crankcase ventilation backpressure, max.
9.5
9.5
9.5
l
Oil volume in turning device
1.7
1.7
1.7
l
Oil volume in speed governor
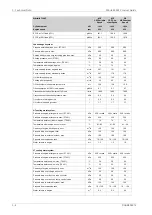
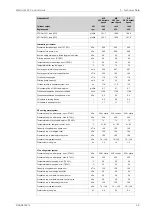
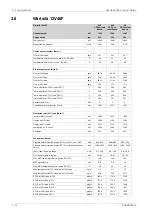
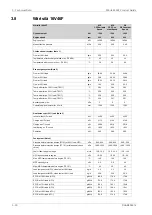
HT cooling water system
250 + static
250 + static
250 + static
kPa
Pressure at engine, after pump, nom. (PT 401)
530
530
530
kPa
Pressure at engine, after pump, max. (PT 401)
74
74
74
°C
Temperature before cylinders, approx. (TE 401)
91...95
91...95
91...95
°C
Temperature after charge air cooler, nom.
150
150
150
m
3
/h
Capacity of engine driven pump, nom.
150
150
150
kPa
Pressure drop over engine, total
100
100
100
kPa
Pressure drop in external system, max.
70...150
70...150
70...150
kPa
Pressure from expansion tank
1.3
1.3
1.3
m
3
Water volume in engine
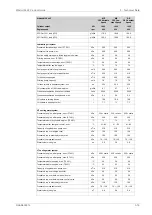
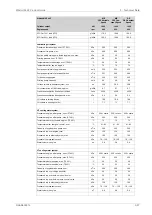
LT cooling water system
250 + static
250 + static
250 + static
kPa
Pressure at engine, after pump, nom. (PT 451)
530
530
530
kPa
Pressure at engine, after pump, max. (PT 451)
38
38
38
°C
Temperature before engine, max. (TE 451)
25
25
25
°C
Temperature before engine, min. (TE 451)
150
150
150
m
3
/h
Capacity of engine driven pump, nom.
50
50
50
kPa
Pressure drop over charge air cooler
20
20
20
kPa
Pressure drop over built-on lube oil cooler
30
30
30
kPa
Pressure drop over built-on temp. control valve
150
150
150
kPa
Pressure drop in external system, max.
70 ... 150
70 ... 150
70 ... 150
kPa
Pressure from expansion tank
0.4
0.4
0.4
m
3
Water volume in engine
3-6
DAAB605814
Wärtsilä 46F Product Guide
3. Technical Data
Summary of Contents for 46F Series
Page 1: ...Wärtsilä 46F PRODUCT GUIDE ...
Page 4: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 8: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 18: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 86: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 104: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 154: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 162: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 170: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 176: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 194: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 200: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 202: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 207: ...Fig 21 7 List of symbols DAAF406507 7 DAAB605814 21 5 21 ANNEX Wärtsilä 46F Product Guide ...