English
English
14
© Titan Tool Inc. All rights reserved.
12. When the set screw is properly seated, install the remaining
three pointed set screws. Do not tighten the set screws.
13. Using a crossing pattern, tighten each of the pointed
setscrews until they are snug. Once all four pointed set screws
are snug, use a crossing pattern to tighten and torque the set
screws to 70–80 in./lbs.
ImPORTANT: It is very important to evenly snug, tighten, and
torque the clutch field pointed set screws in a crossing pattern.
This ensures the clutch field will stay centered in the gear
housing.
15. Line up the three screw holes and dowel pin hole on the
clutch rotor with the screw holes and dowel pin on the drive
shaft assembly hub. Place the clutch rotor onto the hub.
16. Using a 3/16” hex wrench, thread the three socket screws and
lock washers through the clutch rotor and into the drive shaft
assembly hub. Evenly snug, tighten, and torque the socket
screws to 75–85 in/lbs.
17. Make sure the friction surface of the clutch rotor is clean and
free from oil or grease.
18. Locate the two clutch field wires in the control housing.
Gently pull the wires fully into the EPC housing so that there
is no slack in the gear housing. Connect the wires to their
proper terminals on the relay (refer to the labels created
earlier in this procedure or the electrical schematic in the Parts
List section of this manual).
19. Carefully place the heat sink assembly over the control
housing taking care not to pinch any wires.
20. Install the four screws that secure the heat sink assembly to
the control housing. Tighten securely.
mating the Gear Housing and the clutch Housing
1. Place the gear housing assembly onto the cart in front of the
clutch housing. Line up the dowel pins in the gear housing
with their corresponding holes in the clutch housing. Slide
the gear housing assembly onto the clutch housing until there
is no gap between the housings.
2. Thread the four hex screws and lock washers through the
clutch housing and into the gear housing.
3. Using a 12 point, 5/16” wrench, snug and tighten the hex
screws in a crossing pattern. Torque to 140–155 in./lbs.
4. Using a 9/16” socket, thread the hex screw that secures the
gear housing to the cart through the underside of the cart and
into the gear housing. Torque to 100–120 in./lbs.
5. Connect the wire from the EPC housing to its mating
connector on the engine wire harness.
checking the clutch Gap
1. Remove the plastic plug from the top of the clutch housing.
Look through the port to locate the clutch armature and the
clutch rotor.
2. Check the gap between the clutch armature and the clutch
rotor using a .016” feeler gauge and a .035” feeler gauge.
a. Insert each feeler gauge through the port and into the gap between
the clutch armature and the clutch rotor. The .016” feeler gauge
should fit in the gap. The .035” feeler gauge should not fit in the gap.
b. Pull the engine pull cord several times to rotate the clutch armature,
checking the gap with each feeler gauge between each pull.
c. If the .016” gauge does not fit or the .035” gauge does fit at any
checkpoint, the gap must be readjusted. This is done by relocating
the clutch hub and armature assembly on the engine shaft. Refer to
the “Removing/Replacing the Clutch Armature Assembly” procedure.
Servicing the Fluid Section
Use the following procedures to service the valves and repack the
fluid section.
1. Using a Phillips screwdriver, remove the four front cover
screws. Remove the front cover.
2. Start the engine (refer to the procedures in the Operation
section of this manual). Turn the pressure control knob
clockwise to its maximum pressure setting.
3. Toggle the sprayer ON/OFF switch between the ON and
OFF positions in short bursts until the slider assembly and
piston rod stop at the bottom of their stroke (in their lowest
position).
4. Turn off the engine and perform the Pressure Relief Procedure.
Before proceeding, follow the Pressure Relief
Procedure outlined previously in this manual.
Additionally, follow all other warnings to reduce the
risk of an injection injury, injury from moving parts or
electric shock.
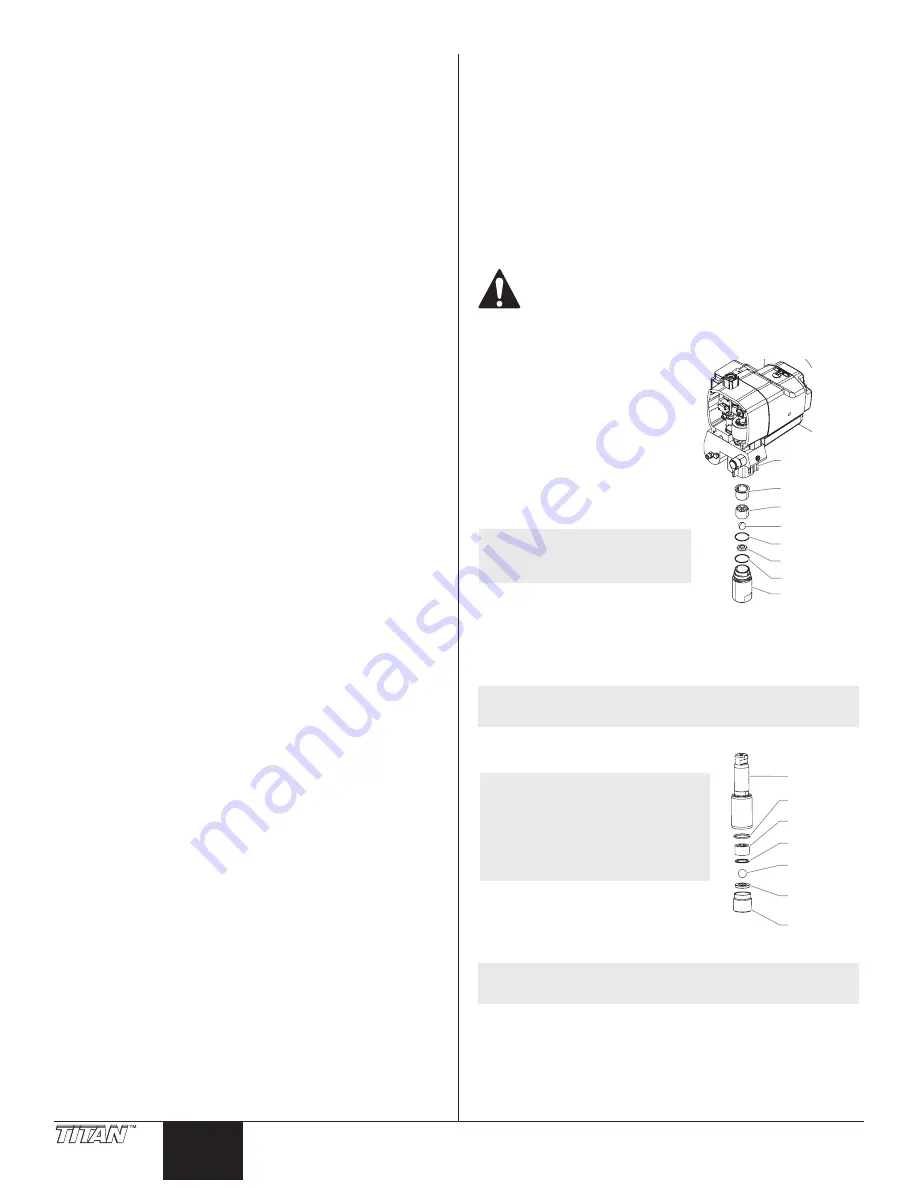
Fluid Section
Housing
Inlet Valve Seal
Inlet Valve Seat
PTFE O-Ring
Inlet Valve
Housing
Piston Bushing
Inlet Cage
Inlet Valve Ball
Servicing the valves
The design of the fluid section allows
access to the inlet valve and seat as well
as the outlet valve and seat without
completely disassembling the fluid
section. It is possible that the valves
may not seat properly because of
debris stuck in the inlet valve seat or
outlet valve seat. Use the following
instructions to clean the valves and
reverse or replace the seats.
NOTE: Keep the sprayer in the
upright position for this
procedure.
1. Using a wrench, loosen and
remove the inlet valve housing
from the fluid section housing.
2. Clean out any debris in the inlet valve housing and examine
the valve housing and seat. If the inlet valve seat is damaged,
reverse the seat to the unused side or replace the seat.
NOTE: If the inlet valve seat is reversed or replaced, the
inlet valve ball must be replaced.
3. Using a 3/8” hex wrench, loosen and remove the outlet valve
retainer from the piston rod.
Outlet Valve
Retainer
Outlet Valve
Seat
Outlet Valve
Ball
Upper Cage
Nylon Washer
Upper Seal
Piston Rod
NOTE: Always service the outlet
valve with the piston rod
attached to the pump.
This will prevent the
piston rod from rotating
during disassembly of the
outlet valve.
4. Clean out any debris and examine
the outlet valve retainer and seat.
If the outlet valve seat is damaged,
reverse to the unused side or
replace the seat.
NOTE: If the outlet valve seat is reversed or replaced, the
outlet valve ball must be replaced.
5. Remove, clean, and inspect the outlet cage and outlet valve
ball. Replace if they are worn or damaged.
6. Reassemble the valves by reversing the steps above.















































