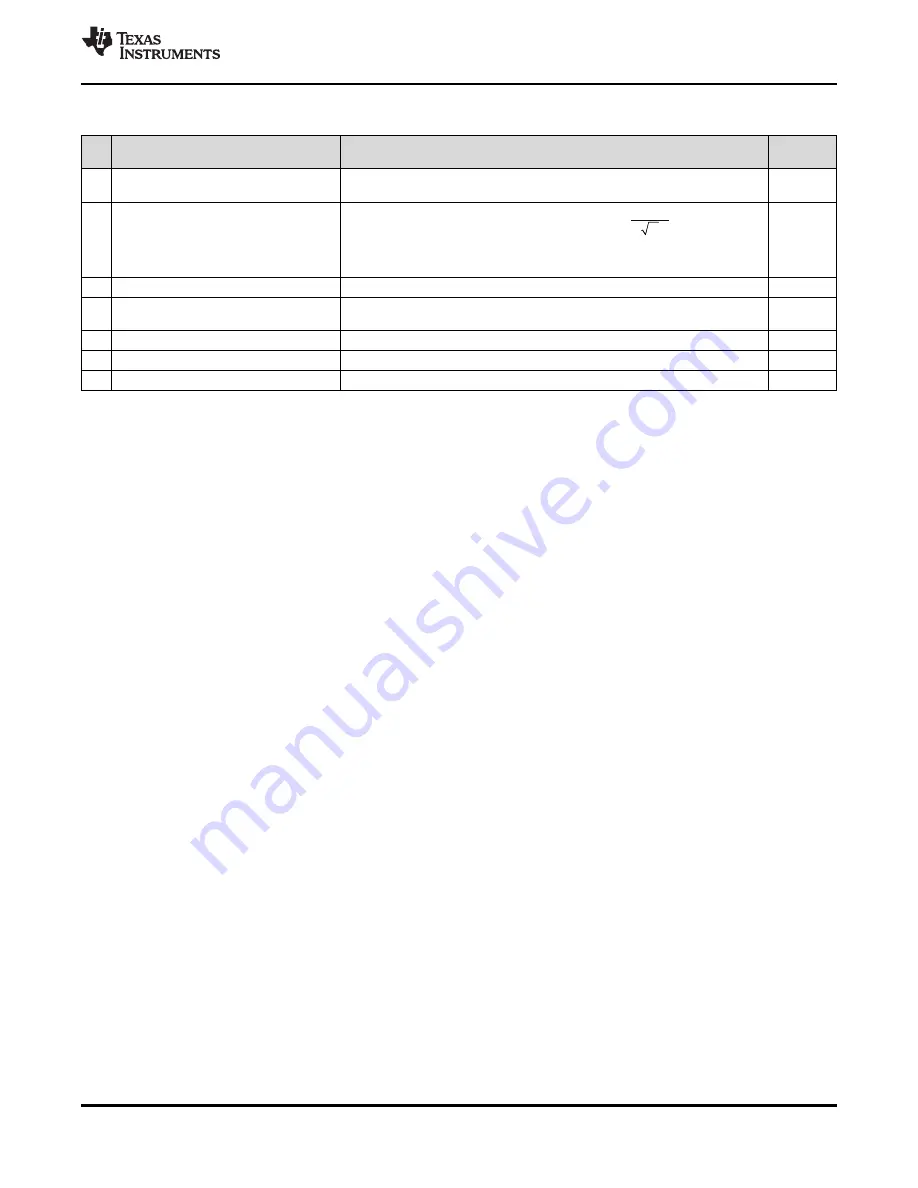
2000 N
Max PLL Lock Time =
m
where N = Pre-Divider Ratio
M = PLL Multiplier
OMAP-L137
www.ti.com
SPRS563G – SEPTEMBER 2008 – REVISED JUNE 2014
Table 6-4. Allowed PLL Operating Conditions
Default
No.
PARAMETER
MIN
MAX
UNIT
Value
PLLRST: Assertion time during
1
N/A
1000
N/A
ns
initialization
Lock time: The time that the application
has to wait for the PLL to acquire locks
OSCIN
2
N/A
N/A
before setting PLLEN, after changing
cycles
PREDIV, PLLM, or OSCIN
3
PREDIV
/1
/1
/32
PLL input frequency
30 (if internal oscillator is used)
4
12
MHz
( PLLREF)
50 (if external clock source is used)
5
PLL multiplier values (PLLM)
(1)
x20
x4
x32
6
PLL output frequency. ( PLLOUT )
N/A
300
600
MHz
7
POSTDIV
/1
/1
/32
(1)
The multiplier values must be chosen such that the PLL output frequency (at PLLOUT) is between 300 and 600 MHz, but the frequency
going into the SYSCLK dividers (after the post divider) cannot exceed the maximum clock frequency defined for the device at a given
voltage operating point.
6.6.2
Device Clock Generation
PLL0 is controlled by PLL Controller 0. The PLLC0 manages the clock ratios, alignment, and gating for the
system clocks to the chip. The PLLC is responsible for controlling all modes of the PLL through software,
in terms of pre-division of the clock inputs, multiply factor within the PLL, and post-division for each of the
chip-level clocks from the PLL output. The PLLC also controls reset propagation through the chip, clock
alignment, and test points.
Copyright © 2008–2014, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
65
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Links:
OMAP-L137
Summary of Contents for OMAP-L137 EVM
Page 221: ......
















































