- 42 -
2. When pushsing operation, be sure to use in "pushing operation".
Also, do not hit the work piece in positioning operation or in the range of positioning
operation.
It causes the breakage and malfunction.
3. Keep the specifications driving speed range for pushing operation.
It causes the breakage and malfunction.
4. The positioning force should be set to “Initial input value”.
(LEY16/25/32/40*:100%, LEY16A*:150%, LEY25A*:200%)
If the positioning force is set below “Initial input value”, it can displace the tack time, which causes
an alarm.
5. Actual speed of the product can be changed by load.
When selecting a product, check the catalog for the instructions regarding selection and
specifications.
6. Do not apply a load, impact or resistance in addition to a transferred load during return to
origin.
Otherwise, the origin can be displaced since it is based on detected motor torque.
7. In pushing operation, set the product to a position of at least 2mm away from a work piece.
(This position is referred to as a pushing start position.)
If the product is set to the same position as a work piece, the following alarm and unstable
operation can occur.
a. ”Posn failde” alarm
The product cannot reach a pushing start position due to the deviation of work pieces in
width.
b. ”Pushing ALM” alarm
The product is pushed back from a pushing start position after starting to push.
8. Do not scratch or gouge the sliding parts of the piston rod, by striking or grasping them
with other objects.
Piston rod is manufactured to precise tolerances, so that even a slight deformation may cause
malfunction.
9. Please connect it so that the impact and load may not be added to the rod from the side
when external guide is used.
10. Please do not operate body itself by the piston rod fixing.
11. When an actuator is operated with one end fixed and the other free (ends tapped or flange
type), a bending moment may act on the actuator due to vibration generated at the stroke
end, which can damage the actuator. In such a case, install a mounting bracket to suppress
the vibration of the actuator body or reduce the speed so that the actuator does not vibrate
at the stroke end.
Also, use a mounting bracket when moving the actuator body or when a long stroke actuator is
mounted horizontally and fixed at one end.
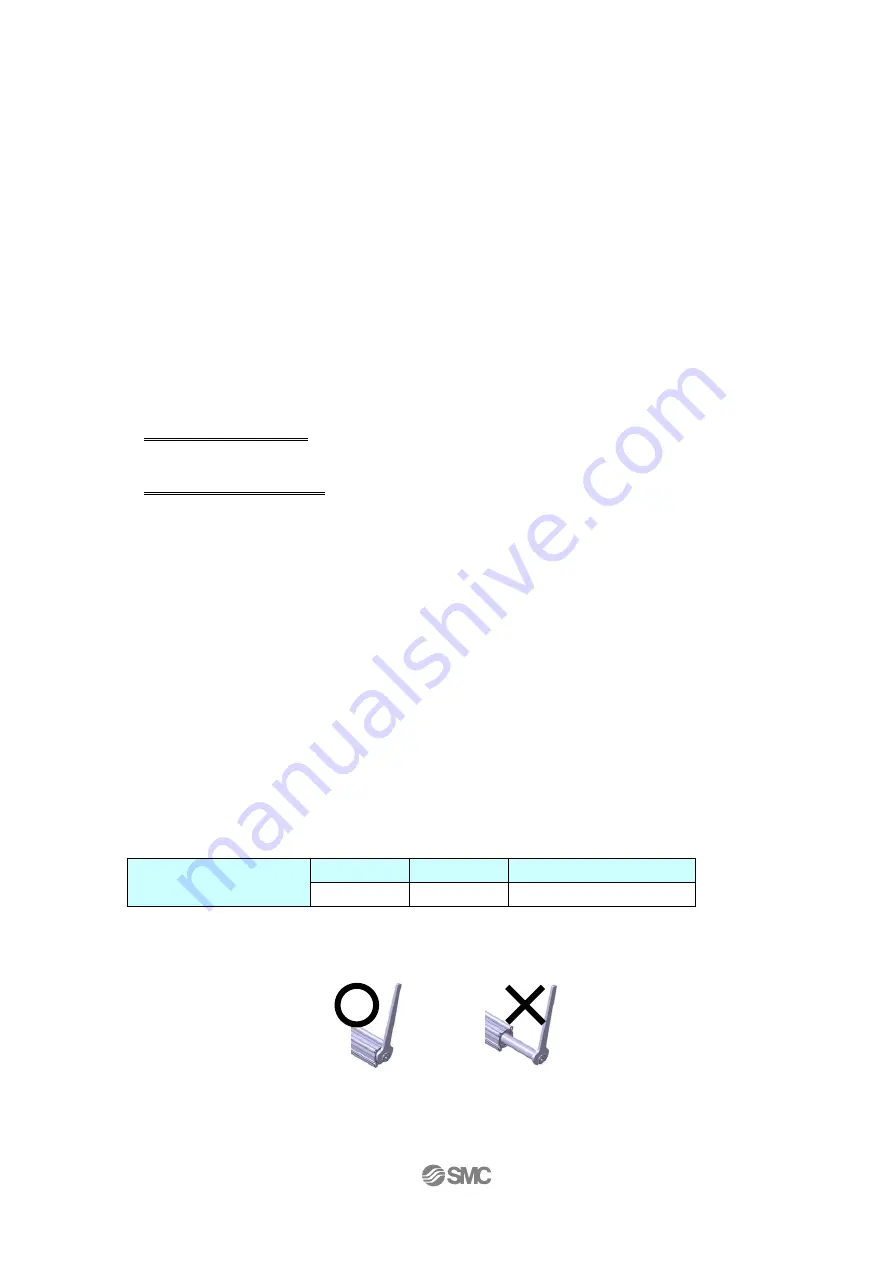
12. Avoid using the electric actuator in such a way that rotational torque would be applied to
the piston rod.
If rotational torque is applied, the non-rotating guide will become deformed, thus affecting the
non-rotating accuracy.
Refer to the table below for the approximate values of the allowable range of rotational torque.
Allowable rotational torque
(N
・
m or less)
LEY16
□
LEY25
□
LEY32
□ / LEY40□
0.8
1.1
1.4
To screw a bracket or a nut onto the threaded portion at the tip of the piston rod, make sure to
retract the piston rod entirely, and place a wrench over the flat portion of the rod that protrudes.
Tighten it by giving consideration to prevent the tightening torque from being applied to the
non-rotating guide.




























