Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) 4-3
protocol over IP. ATMP is more efficient than PPTP for network-to-network tunnels.
■
IPsec
stands for IP Security, a set of protocols that suppor ts secure exchange of IP packets at the IP layer.
IPsec is deployed widely to implement Vir tual Private Networks (VPNs). IPsec suppor ts two encr yption
modes: Transpor t and Tunnel. Transpor t mode encr ypts only the data por tion (payload) of each packet, but
leaves the header untouched. The more secure Tunnel mode encr ypts both the header and the payload. On
the receiving side, an IPsec-compliant device decr ypts each packet. The Netopia Firmware Version 5.4
suppor ts the more secure Tunnel mode.
DES
stands for Data Encr yption Standard, a popular symmetric-key encr yption method. DES uses a 56-bit
key. The Netopia Firmware Version 5.4 offers IPsec DES encr yption over the VPN tunnel.
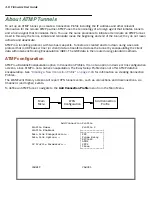
When used to initiate the tunnelled connection, the Router is called a
PPTP Access Concentrator
(
PAC
, in PPTP
language), or a
foreign agent
(in ATMP language). When used to answer the tunnelled connection, the Netopia
Router is called a
PPTP Network Ser ver
(
PNS
, in PPTP language) or a
home agent
(in ATMP language).
In either case, the Netopia Router wraps, or encapsulates, information that one end of the tunnel exchanges
with the other, in a wrapper called General Routing Encapsulation (GRE), at one end of the tunnel, and unwraps,
or decapsulates, it at the other end.
Configuring the Netopia Router for use with the different protocols is done through the console-based menu
screens. Each type is described in its own section:
■
"About PPTP Tunnels" on page 4-4
■
"About IPsec Tunnels" on page 4-7
■
"About ATMP Tunnels" on page 4-8
Your configuration depends on which protocol you (and the router at the other end of your tunnel) will use, and
whether or not you will be using the VPN client software in a standalone remote connection.
Note:
You must choose which protocol you will be using, since you cannot both expor t PPTP and use ATMP, or
vice versa, at the same time.
Having both an ATMP tunnel and a PPTP expor t is not possible because functions require GRE and the router’s
PPTP expor t/ser ver does not distinguish the GRE packets it for wards. Since it processes all of them, ATMP
tunneling is impaired. For example, you cannot run an ATMP tunnel between two routers and also have PPTP
expor ted on one side.
Summary
A Vir tual Private Network (VPN) connects the components of one network over another network. VPNs
accomplish this by allowing you to
tunnel
through the Internet or another public network in a manner that
provides the same security and features formerly available only in private networks.
VPNs allow networks to communicate across an IP network. Your local networks (connected to the Netopia
Router) can exchange data with remote networks that are also connected to a VPN-capable router.
This feature provides individuals at home, on the road, or in branch offices with a cost-effective and secure way
to access resources on remote LANs connected to the Internet with Netopia Routers. The feature is built
around three key technologies: PPTP, IPsec, and ATMP.
Summary of Contents for 4000 Series
Page 10: ...x Firmware User Guide Packet header types B 14 Appendix C Binary Conversion Table C 1 Index ...
Page 18: ...1 8 Firmware User Guide ...
Page 66: ...2 48 Firmware User Guide ...
Page 102: ...3 36 Firmware User Guide ...
Page 130: ...4 28 Firmware User Guide ...
Page 206: ...7 18 Firmware User Guide ...
Page 224: ...9 14 Firmware User Guide ...
Page 274: ...10 50 Firmware User Guide ...
Page 314: ...Index 6 ...