Technical Information
75
DGC 6xxx
is activated piezoelectrically (i.e. by pressure).
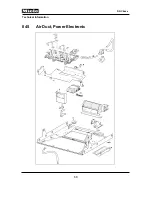
The EPI electronic (Figure 045-1, Item 1) of the wireless roast probe
thermometer transmits and receives all frequencies in the high-frequency ISM
band between 433.05MHz and 434.79MHz to use for temperature
measurement. This transmission/reception runs sequentially and constantly
(but with a millisecond delay between transmission and reception).
The frequency band is subdivided so that one frequency corresponds to only
one temperature. The high-frequency signal activates the sensor element
(Figure 045-1, Item 4.2) inside the roast probe in order to generate an
acoustic surface wave.
An acoustic surface wave (engl. “SAW” for
s
urface
a
coustic
w
ave) is an
impact sound wave that breaks smoothly across a surface.
This surface wave is very sensitive to temperature changes. These changes
produce a shift in the reflected surface wave and generate a change in the
reflected high-frequency (HF) signal. This modified HF signal uses the
electronic for temperature measurement, in which it compares the transmitted
signal to the received signal.
2.8.3
Frequency Transmission/Reception in the “Wireless Roast Probe”
System
1. The electronic (Figure 045-1, Item 1) generates a high-frequency signal
that is converted by the antenna (Figure 045-1, Item 3) into an
electromagnetic wave.
2. The antenna (Figure 045-1, Item 4.1) converts the electromagnetic wave
back into a high-frequency signal.
3. The high-frequency signal generates an acoustic surface wave in the
piezoelectric element (Figure 045-1, Item 4.3).
4. The acoustic surface wave is reflected by the reflectors (Figure 045-1,
Item 4.4), which generates a resonator frequency.
5. The resonator frequency changes with the current cavity temperature.
This change in resonator frequency is used for temperature
measurement.
6. The resonator frequency is converted back into a high-frequency signal
and sent back via the antenna (Figure 045-1, Item 4.1) to the electronic
(Figure 045-1, Item 1).
7. A change in the received high-frequency signal equals a change in the
measured cavity temperature.
Summary of Contents for DGC 6 Series
Page 1: ...TECHNICAL INFORMATION DGC 6xxx Combi Steam Ovens 2018 Miele USA ...
Page 15: ...Technical Information 15 DGC 6xxx 010 Casing ...
Page 23: ...Technical Information 23 DGC 6xxx 020 Door ...
Page 27: ...Technical Information 27 DGC 6xxx 030 Cavity ...
Page 43: ...Technical Information 43 DGC 6xxx 035 Steam Generator Convection Fan ...
Page 57: ...Technical Information 57 DGC 6xxx Figure 035 14 Terminal Block ...
Page 58: ...Technical Information 58 DGC 6xxx 040 Water Container Drive ...
Page 68: ...Technical Information 68 DGC 6xxx 045 Air Duct Power Electronic ...