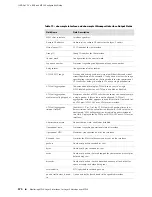
host1(config-if)#
vlan id X
If you configure such a setting, the set of commands that is configured first takes
precedence. Consider the following two cases with this configuration:
■
Case 1: Assume that svlan id X any 8100 is configured on the subinterface. In
this case, all packets with the outer tag as X and Ethertype as 8100 are matched
to the sub-interface.
■
Case 2: Assume that vlan id X is configured on the subinterface. In this case,
only single-tagged packets with VLAN ID X and Ethertype of 8100 are matched
to this subinterface. For VLAN ID of 0, the untagged traffic and the priority tagged
traffic are matched the subinterface. This behavior is how it works in existing
implementation.
If the S-VLAN subinterface is configured with any value other than an Ethertype 8100,
both S-VLAN and VLAN interfaces for the same ID can be configured together as
listed earlier. In such cases, the packets are expected to arrive with an S-VLAN ID
other than 0x8100 and the C-VLAN Ethertype as 0x8100, which helps to uniquely
identify the subinterface for all the following traffic patterns:
■
Untagged
■
C-VLAN tag only
■
S-VLAN tag only
■
Both S-VLAN and C-VLAN tagged
The following set of commands generates in appropriate error messages when you
attempt to configure them on a VLAN major interface:
host1(config-if)#
interface fastEthernet 1/1.1
host1(config-if)#
svlan id X anyUntagged
host1(config-if)#
svlan Ethertype 0x8100
host1(config-if)#
interface fastEthernet 1/1.2
host1(config-if)#
vlan id X
where
X
represents a valid V-LAN ID.
The following examples are valid configurations on a VLAN major interface:
host1(config-if)#
interface fastEthernet 1/1.1
host1(config-if)#
svlan id X anyUntagged
host1(config-if)#
svlan Ethertype 0x8100
host1(config-if)#
interface fastEthernet 1/1.2
host1(config-if)#
vlan id Y
host1(config-if)#
interface fastEthernet 1/1.3
host1(config-if)#
svlan id X X
where the V-LAN ID value,
X
, is not the same as
Y
.
Related Topics
S-VLAN Subinterface with an Untagged C-VLAN ID Overview on page 524
■
■
svlan id
S-VLAN Subinterface with an Untagged C-VLAN ID Examples
■
559
Chapter 7: Configuring Layer 2 Services over MPLS
Summary of Contents for BGP
Page 6: ...vi ...
Page 8: ...viii JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 37: ...Part 1 Border Gateway Protocol Configuring BGP Routing on page 3 Border Gateway Protocol 1 ...
Page 38: ...2 Border Gateway Protocol JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 234: ...198 Monitoring BGP JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 236: ...200 Multiprotocol Layer Switching JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 542: ...506 Monitoring BGP MPLS VPNs JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 544: ...508 Layer 2 Services Over MPLS JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 610: ...574 Virtual Private LAN Service JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 624: ...588 VPLS References JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 680: ...644 Virtual Private Wire Service JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 724: ...688 Monitoring MPLS Forwarding Table for VPWS JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 725: ...Part 6 Index Index on page 691 Index 689 ...
Page 726: ...690 Index JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...